Table of Contents
Capacitor and its Principle:
What is Capacitor?
It is an arrangement used for storing large amounts of electric charge and hence electric energy.
An arrangement of two conductors separated by a dielectric medium is said to form a capacitor or condenser. It is of three types-
- If the conductors are plane, the capacitor is called parallel plate capacitor.
- If the conductors are spherical, the capacitor is called spherical capacitor.
- If the conductors are cylindrical, it is called cylindrical capacitor.
Principle of Capacitor:
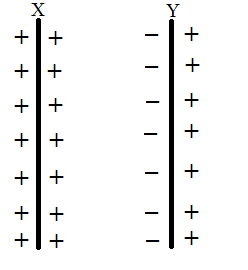
Let us take a plate X. Give some charge to plate X, till its potential becomes maximum. Now consider another plate Y, held near plate X. Due to the phenomenon of induction, a negative charge is induced on the inner side of plate Y and an equal positive charge is induced on the outer side of plate Y. As the negative charge on the plate Y is nearer to plate X, hence it is more effective. The negative charge on plate Y will reduce the positive charge on plate X. Hence the potential of plate X decreases. In other words, the capacity of plate X increases. Now connect the plate Y to earth, all the positive charges on plate Y will go to earth. Now the negative charge on plate Y will further reduce the positive charge on plate X. Hence the potential of plate X further decreases. In other words, the capacity of plate X increases.
Thus, when we bring an uncharged earth-connected rod near a charged rod, the capacity of charged rod increases.
Uses of Capacitor:
Capacitors are used in-
- Oscillator circuits.
- In radio tunning.
- In filter circuits.
- In electric motor etc.







Comments (No)