Table of Contents
Electrical Properties of Colloidal Sols:
Generally, colloidal particles of sol are electrically charged and all the particles of a given sol carry the same charge (either +ve or -ve). The dispersion medium has an equal and opposite charge. The two important electrical properties of colloidal sols are-
Electrophoresis or Cataphoresis:
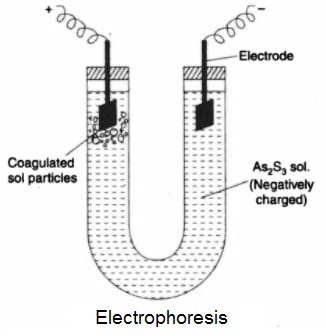
The phenomenon of the migration of colloidal particles towards oppositely charged electrode (cathode or Anode) under the influence of an applied electric field is known as Electrophoresis. This process is carried out in a U-shaped glass tube containing colloidal sol in which two Pt-electrodes are fitted. When an electric field is set up in the tube, the charged colloidal particles start moving towards the cathode or anode depending upon the sign of their charge. For example- when a positively charged Fe(OH)3 sol is taken in the tube, the colloidal particles will move towards the cathode and if negatively charged As2S3 sol is taken in the tube, then colloidal particles move towards the anode.
Application of Electrophoresis:
- Coating rubber on metallic articles. Example- on electrical wires.
- Removing the sludge from sewage waste.
- Removing carbon particles from smoke by using Cottrell smoke precipitators.
Electro-osmosis:
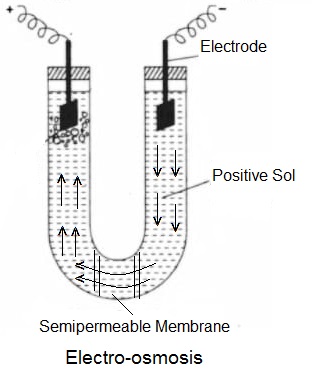
The phenomenon of the migration of dispersion medium particles under the influence of an applied electric field when the dispersed phase particles are prevented from moving is known as Electro-osmosis. The movement of dispersed phase particles is prevented by placing a suitable semipermeable membrane (diaphragm) in the U-shaped glass tube containing colloidal sol and fitted with Pt-electrodes. When an electric field is set up in the tube, the particles of the dispersion medium will move towards the respective electrode in a direction opposite to that in which the dispersed phase colloidal particles move. For example- when a positive sol is placed in the tube, the dispersion medium particles will move towards the anode.








Comments (No)