Table of Contents
Bohr Theory of Atomic Structure:
- Bohr’s model is valid only for mono-electronic systems like H, He+, Li2+.
- It is basically an intuitive model.
- It is given by Neil Bohr, 1913.
- This model explains the line spectrum of hydrogen atom.
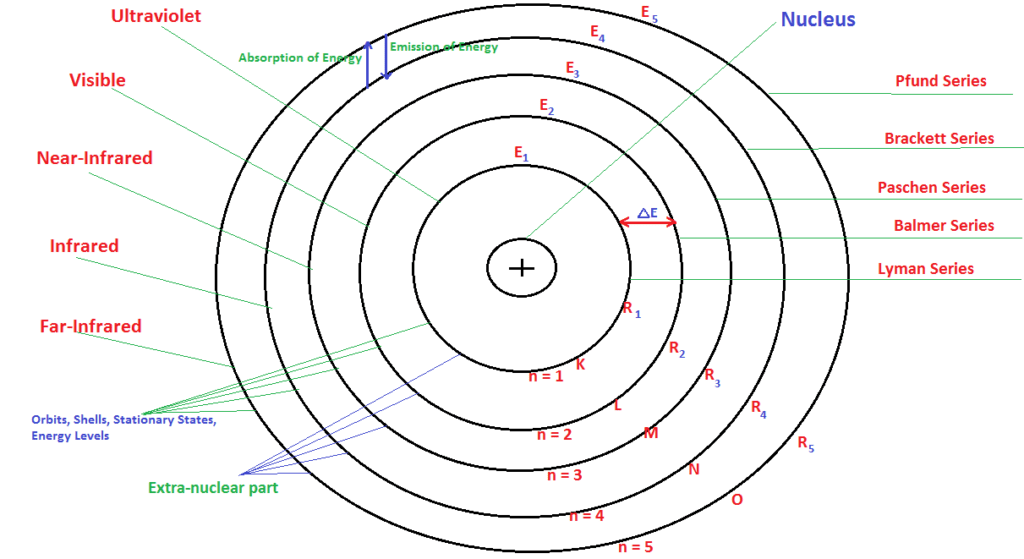
Postulates of Bohr Theory of Atomic Structure:
- Atom consist of two parts-
- The very small, centralized, and highly denser position is called a Nucleus.
- Extra-nuclear part containing electrons, moving around the nucleus in well-defined circular path called as orbits.
- Electrons revolve around the nucleus with high velocity, in those orbits for which angular momentum is quantized.
i.e mvr = nh/2π
where, ‘n’ = 1, 2, 3,…………. but in friction; ‘v’ is the velocity; ‘m’ is mass of the electron; ‘r’ is the radius of the nth orbit
- Different energy levels are numbers as 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or K, L ,M, N, O.
- The energy of the electron is constant in fixed orbit known as Stationary States or Energy Levels.
- As the size of shell increases, energy increases but energy gap decreases (away from the nucleus energy increase from more negative to less negative and finally become zero).
- An electron can jump from any lower to any higher orbit, by absorbing energy is equal to the energy difference of two orbits.
- An electron can jump from any higher to any lower orbit, by emitting or releasing energy is equal to energy difference of two orbits.
- During absorption or emission of energy, Planck’s quantum equation is obeyed i.e. E = hν, where ‘ν‘ is the frequency of radiation absorbed or emitted and ‘h’ is Planck’s constant.
- Ionization energy is equal and opposite to the energy of electron in that orbit i.e. I.E. = -En.
Limitations of Bohr’s Model of Atom:
- Inability to explain the line spectra of multi-electron atoms.
- It fails to explain the multiple or fine structure of spectral lines.
- Splitting of lines under the influence of a strong magnetic field or electric field (Zeeman Effect and Stark Effect).
- It violates de Broglie concept of dual character of matter.
- It violates Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle.
- Bohr theory never explains the union of atom to form molecules.
- Inability to explain the shape of molecule.
- It cannot explain the brightness of spectral lines.
- Bohr gives a flat model of the atom and the concept of orbit considering the electron as a particle but nowadays it is believed that atom possesses 3D model and concept of orbitals.
- Constituents Of Air And Their Uses
- Air Pollution- Causes, Effects, and Control Measures
- Water Pollution- Causes, Effects, and Control Measures
- Solid Waste Management
- Electrochemistry Notes From Tamil Board








Comments (No)