Table of Contents
C++ Data Types:
A data type is a term that is used to show the kind of data values or the type of data that is expected to be handled. A data type is, therefore, a group of data values that are-
- Governed by the same set of rules.
- Operated by the same set of operators.
- Occupy the same number of bytes in the memory.
C++ like any other language provides ways and facilities to handle different types of data by providing data types. C++ language supports three data types-
- Built-in data types (also known as basic or fundamental types).
- User-defined data types.
- Derived data types.
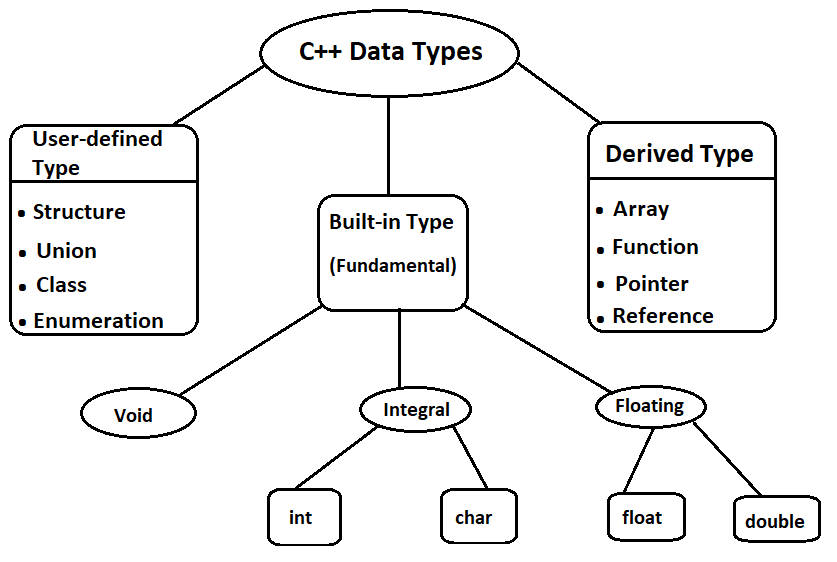
Built-in Data Types:
The built-in data types available in C++ are-
- Integral Type.
- Floating Type.
- Void.
These are also called basic or fundamental data types. The size and range of these data types vary from computer to computer. The fundamental data types are the data types at the lowest level, i.e., those which are used for actual data representation in memory.
Integral Type:
Integral type can be further classified into-
- int
- char
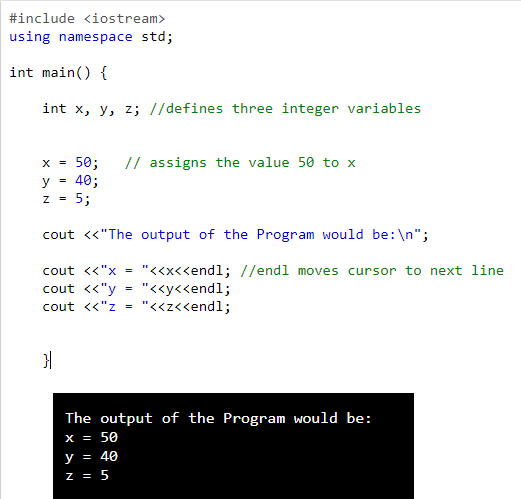
int data type- An integer is an integral whole number without a decimal point. These numbers are used for counting. For example 26, 373, –1729 are valid integers. Normally an integer can hold numbers from -32768 to 32767. However, if the need is, a long integer (long int) can also be used to hold integers from -2, 147, 483, 648 to 2, 147, 483, 648.
| Program to demonstrate the use of Integer variables: |
char data type- Characters can store any member of the C++ implementation’s basic character set. A character is a non-numeric data type consisting of a single alphanumeric character enclosed between two apostrophes, i.e., single quotation marks. Examples of valid character types are ‘A’, ‘7’, ‘a’, ‘6’, ‘&’.
It may be noted here that 6 and ‘6’ are of different data types. The former is of type int and later of type char.
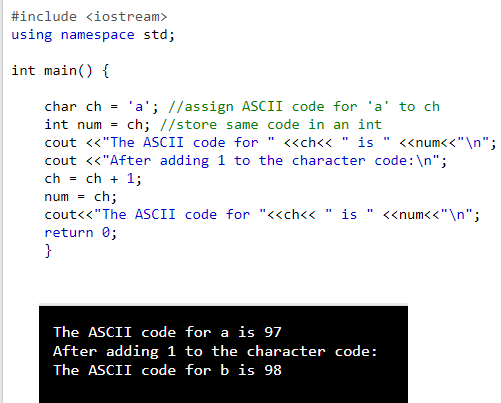
Char type is often said to be an integer type. It is clear from the above program. It is because the alphabets, symbols, etc. are stored in computer memory by ASCII codes. It must be clear that the ASCII code of ‘A’ is 65, ‘a’ is 97, ‘B’ is 66, ‘b’ is 98, ‘6’ is 54, ‘7’ is 55 and ‘0’ is 48.
| Program to display ASCII code of a character and vice versa: |
Floating Type:
A floating point number is represented in two ways i.e. decimal form and exponent form. It can be further classified into-
- float
- double
Float Data type:
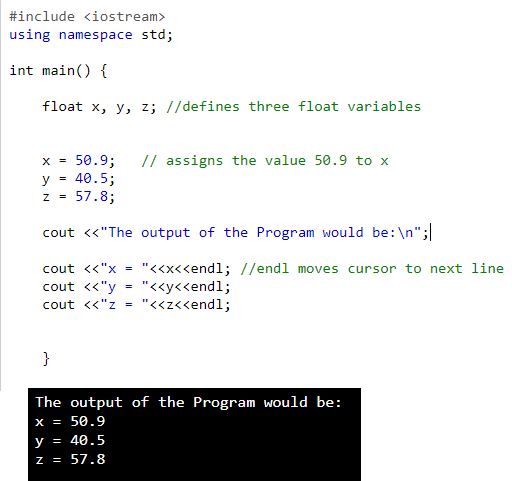
Decimal Form- The floating point number in this form has a decimal point in it. A decimal point must be present even if the number has an integral value. These numbers are used for measurement. Example- height, area, distance, etc.
Examples of valid floating point numbers in decimal form are:
| 27.4 -927. 40.03 0.006 |
Examples of invalid floating point numbers in decimal form are:
| 4,297.98 (comma not allowed) -39 (No decimal point) |
| Program to demonstrate the use of Float variables in Decimal Form: |
Exponent Form- Another way of representing a floating point number in C++ is exponent form. In this form, the number is broken into two parts: mantissa and exponent. The mantissa is a floating point number in decimal form. The exponent starts with the letter “e” followed by an integer (signed or unsigned). For example- floating point number 7356.8 can be written as 7.3568 x 103. In exponent form, the base 10 of the decimal number system is replaced by the character e or E. So 7.3568 x 103 will be written as 7.3568 e 3.
Examples of valid floating point numbers in exponent form are:
| 314.27e09 2.967e-98 -87.98e21 84.00765e+8 |
Examples of invalid floating point numbers in exponent form are:
| 3.937 e 1.3 (exponent has decimal point) -26.89 e (exponent has no digit) |
| Program to demonstrate the use of Float variables in Exponent Form: |
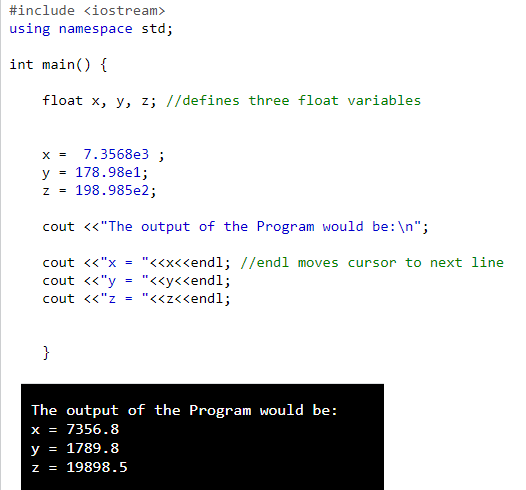
Floating point numbers have two advantages over integers. First, they can represent values between the integers. Second, they can represent a much greater range of values. But floating-point numbers suffer from one disadvantage also. Floating-point operations are usually slower than integer operations.
Double data type:
The word double stands for double precision floating point. The meaning of precision is the number of digits after the decimal point. It is also used for handling floating-point numbers. It is capable of representing floating-point numbers with a much larger range. It occupies twice as much memory as type float. It is used when the type float is too small or insufficiently precise.
The double data type is larger and slower than the float data type. So one must always use the smallest variable type for strong values in a C++ program to make it efficient.
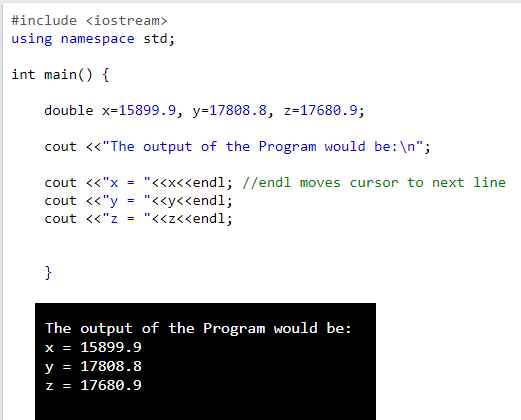
| Program to demonstrate the use of Double data type: |
Void Data Type:
The void data type specifies an empty set of values. The void data types have two important purposes:
- Indicates that a function does not return a value.
- Declares a generic pointer.
No object of type void may be declared.
For example, we may define a function in C++ as:
This indicates that the function main () does not return any useful value.
| Data Types | Memory Size | Range |
|---|---|---|
| char | 1 byte | -128 to 127 |
| signed char | 1 byte | -128 to 127 |
| unsigned char | 1 byte | 0 to 255 |
| short | 2 byte | -32,768 to 32,767 |
| signed short | 2 byte | -32,768 to 32,767 |
| unsigned short | 2 byte | 0 to 65,535 |
| int | 2 byte | -32,768 to 32,767 |
| signed int | 2 byte | -32,768 to 32,767 |
| unsigned int | 2 byte | 0 to 65,535 |
| float | 4 byte | 3.4e-38 to 3.4e38 |
| double | 8 byte | 1.7e-308 to 1.7e308 |
| long double | 10 byte | 3.4e-4932 to 3.4e4932 |








Comments (No)