Table of Contents
Methods of Producing Induced EMF:
There are three methods of producing induced EMF-
By Changing the Magnitude of Magnetic Field B:
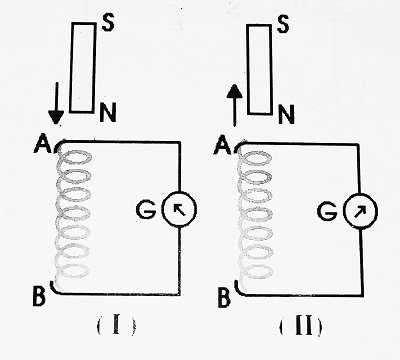
Take a coil AB. The ends of the coil are connected with Galvanometer (G). Take a bar magnet with its N-pole towards the coil.
When we move the magnet towards the coil, the galvanometer shows deflection towards the left (say) and when we move the magnet away from the coil, the galvanometer shows deflection towards the right (say). Also, when we keep the magnet stationary near the coil, the galvanometer shows no deflection.
When we move the magnet towards the coil, magnetic flux linked with the coil increases (changes) and when we move the magnet away from the coil, magnetic flux linked with the coil decrease (changes). Also, when we keep the magnet stationary near the coil, the magnetic flux linked with the coil remains constant.
Thus, when there is a change in magnetic flux linked with the coil, an induced EMF is produced in the coil.
Another Experiment: Let us consider two circuits placed close to each other. One circuit contains battery B and key K. This circuit is called a primary circuit. The other circuit contains galvanometer G and is called a secondary circuit.
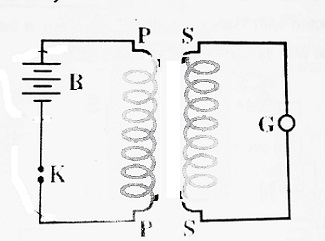
When we press key K, of the primary circuit, galvanometer G shows momentary deflection in one direction and when we switch off key K of the primary circuit, galvanometer G again shows momentary deflection in opposite direction. If the current is allowed to flow continuously in the primary circuit, then there will be no deflection in the galvanometer.
When we press the key K of the primary circuit, magnetic flux linked with the secondary circuit increases (changes) and when we switch off the key K of the primary circuit, magnetic flux linked with the secondary circuit decreases (changes) and when the current is allowed to flow continuously in the primary circuit, magnetic flux linked with secondary circuit remains constant.
Thus, when magnetic flux linked with the primary circuit changes, an induced EMF is produced in the secondary circuit.
By Changing the Area A:
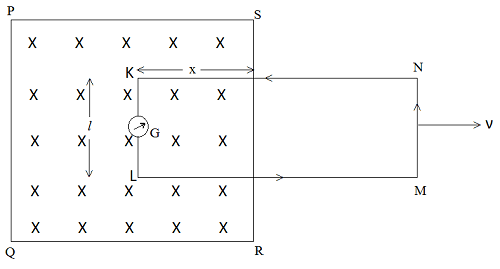
Suppose a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to the plane of the paper and directed outwards (shown by crosses) is confined in region PQRS. Let a rectangular wire loop KLMN is held partially in the magnetic field B. Let KL = l and ‘X’ be the portion of the loop in the magnetic field. When the loop KLMN is taken out, the area of the loop changes and also magnetic flux linked with the loop also changes and hence induced EMF is produced in the loop KLMN. Suppose in time dt, the loop is moved out through a small distance dx.
| Decrease in area of the loop (ds) = –l . dx Decrease in magnetic flux linked with the loop (dΦ) = B . ds = -Bldx As induced e.m.f, e = -dΦ/dt = Bldx/dt = Blν [∵ ν = dx/dt, the velocity of loop] |
This is the required expression for induced EMF in this case. The direction of this induced EMF is given by Fleming’s right-hand rule.
By Changing the Relative Orientation of the Coil and Magnetic Field:
When a coil is rotated in a magnetic field, the magnetic flux linked with the coil changes. Therefore, an induced EMF is produced in the coil.









Comments (No)