Table of Contents
Bonding and Anti-Bonding Molecular Orbitals:
Molecular orbitals are the linear combination of atomic orbitals with a maximum overlap which produces as many molecular orbitals as the number of combining atomic orbitals. Thus, when two atomic orbitals overlap each other, two molecular orbitals are formed i.e. Bonding molecular orbital and anti-bonding molecular orbital. Let us consider the combination of two 1s atomic orbitals of two H-atoms to form two molecular orbitals in a molecule of H2. Since an electron has a wave nature; the crests of the electron wave are usually given a positive sign and the troughs a negative sign. Due to the wave nature of the electron, atomic orbitals can combine in two ways-
Combination of Atomic Orbitals by Addition:
Here, the crest of one wave overlap with the crest of the other or trough of one wave overlaps with the trough of the other so that the two-electron waves representing two atomic orbitals are on the same side of the imaginary horizontal line i.e. there is in-phase overlap which results in the formation of a molecular orbital as shown below-
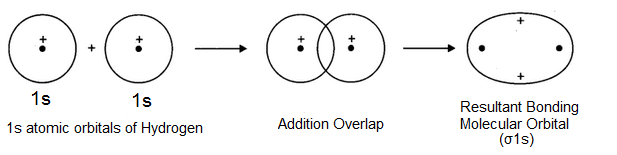
The molecular orbital thus formed has a high electron density in between the two nuclei which shields them from mutual repulsions and hold them together and closer at an equilibrium distance known as Bond length. Such a molecular orbital formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals with the same sign is known as Bonding molecular orbital and is of lower energy than the combining atomic orbitals. It is designated as σ1s molecular orbital. σ reveals the symmetrical nature of the molecular orbital about the molecular axis joining the two nuclei.
Combination of Atomic Orbitals by Subtraction:
Here, the crest of one wave overlap with the trough of the other so that the two-electron waves representing atomic orbitals lie on opposite sides of the imaginary horizontal line (one on the positive side and the other on the negative side) i.e. there is out of phase overlap resulting in the formation of a molecular orbital as shown below-
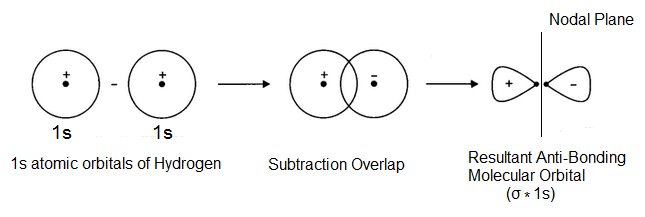
The two waves being oriented in opposite directions cancel out each other due to which electronic charge is concentrated beyond the nuclei and almost zero between the two nuclei (as there is a node). So the electrons feel less attraction and the nuclei will be repelled away from each other. Such a molecular orbital which is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals with opposite sign is known as anti-bonding molecular orbital and is of higher energy than the combining atomic orbitals. It is designated as σ∗1s.









Comments (No)