Table of Contents
Cellular Totipotency:
Meaning: Totipotency is the ability of a somatic cell to produce a complete organism.
Isolated single plant cells can multiply in a culture medium under aseptic conditions. In a specific environment, these daughter cells may develop and differentiate into embryoids similar to normal embryos that grow into independent plants. Such cells are called totipotent. These possess all the hereditary information and potentialities present in the zygote.
Examples: Fertilized ovum and a small excised portion of planaria and sponge cells regenerate into a new organism.
Basis- The concept of totipotency was based on the understanding that each cell of an organism is derived from the fertilized egg. It must contain a complete set of genes in its nucleus and all the inherent capacity to produce the whole organism.
The undifferentiated cells of primary meristems of stem and root tip are totipotent. But the cells from differentiated tissues such as pith, secondary phloem, mesophyll and endosperm can also grow into an undifferentiated mass of identical cells called callus. When callus shows differentiation into root and shoot, the structures are called embryoids.
Embryoids are nonzygotic embryo-like structures that are formed in vitro culture and have the potential to develop into plants. These are called somatic embryos because they develop from diploid vegetative cells. The embryoids grow into typical plants like normal embryos.
Steward’s Experiment:
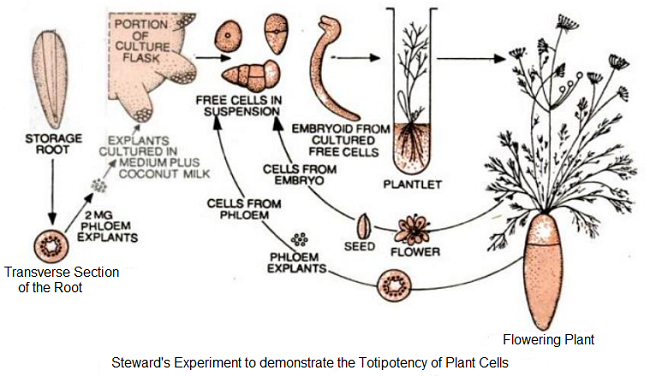
Cellular totipotency was first proposed by German botanist Haberlandt in 1902. He thought that since each cell of the organism is derived from the fertilized egg and contains the same hereditary information, it should be able to regenerate the whole plant. However, Haerlnadt’s experiment to grow isolated green cells failed. Success to grow isolated cells was achieved by Steward and his coworkers (1957) of Cornell University, U.S.A. They took 2 mg pieces of phloem tissue of mature carrot roots in a special flask containing liquid medium supplemented with coconut milk. By gently shaking the culture, the callus separates into isolated cells and groups of cells floating in the culture medium. Some of these cell clusters developed roots. When these embryoids were transferred to a semisolid nutrient medium, each one developed into a whole plant that developed flowers and produced seeds.
Steward and his co-workers (1963) and Halperin and Wetherell (1964) demonstrated that in carrots, the callus raised from an immature embryo can be made to differentiate into several embryoids. The callus is placed in a liquid culture medium and is rotated continuously so that its cells get isolated. When rotation is stopped, each cell grows out into an embryoid. Steward estimated that as many as 1,00,000 embryoids can be obtained from a single carrot embryo and each of these embryoids can grow into a normal flowering plant.
From the above experiments, Steward concluded that:
(1) The mature cells when freed from the plant body are capable of forming new plants.
(2) Only the isolated single cells i.e., the cells free from the inhibiting effect of adjacent cells can grow in a culture medium into a normal adult plant.
(3) During the development of a normal plant from a single isolated cell in culture, stages resembling to globular heart-shaped and torpedo-shaped embryos are formed. This indicates that this also involves all regular stages of embryonic development.
Application of Tissue Culture:
(1) Tissue culture is a method of rapid multiplication or asexual reproduction, especially for rare plants which reproduce through seeds with difficulty.
(2) Virus-free plants can be grown from virus-infected plants through shoot culture.
(3) Embryo culture overcomes seed dormancy and helps in producing viable plants from hybrid crosses.
(4) Haploid plants and from them, homozygous plants can be successfully produced.
(5) Somatic cell hybrid plants can be grown by tissue culture. This is called protoplast culture.
(6) It shortens the period of development of new varieties.
(7) Development of plants resistant to weedicides.









Comments (No)