Table of Contents
Excretory System of Man:
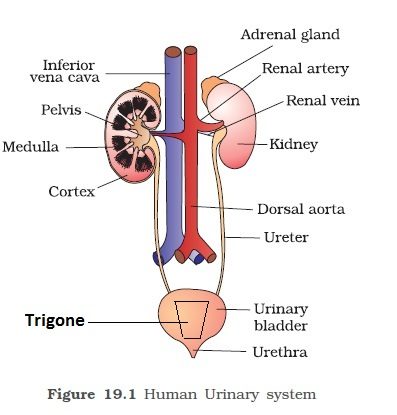
The excretory system of man consists of a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra.
Kidneys:
Appearance and Position:
The kidneys are dark red, a bean-shaped organ about 10-13 cm long, 5-6 cm in breadth and 3-4 cm wide, weighing about 150-170 gm in adult male and 135-145 gm in the female. They are placed against the back wall of the abdominal cavity, below the diaphragm. The lower two pairs of ribs protect them and they are covered by Peritoneum on the ventral side only. The left kidney is slightly larger than the right and also lies at a higher level. Each kidney on the medial side has a concavity called Hilus. Blood vessels, lymph vessels, nerves, and ureters enter or leave the kidney through hilus. The kidneys are metanephric in mammals.
Structure:
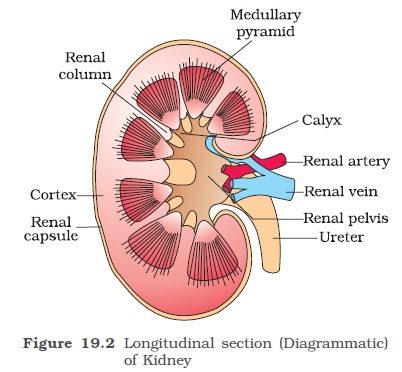
The kidney is composed of a large number of microscopic coiled structures called nephrons or uriniferous tubules. A nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. The nephrons are held together by connective tissues. Nephrons are covered by a capsule of white fibrous tissues which is also covered by a layer of fat tissue known as adipose tissues followed by a layer of fibrous membrane renal fascia. The adipose tissue forms a shock-absorbing cushion and renal fascia fixes the kidneys with the abdominal wall. The outer region of the kidney is called the renal cortex and the inner region is called the renal medulla. The medulla is divided into 15-16 conical masses, the renal pyramids each bearing renal papilla towards the pelvis. The renal papilla projects into the cavity of the minor calyx into the funnel-shaped structure known as pelvis which cortex extends into the medulla as renal columns of Bertin.
Ureters:
From the hilum of each kidney, there arises a slender, white tube 25-30 cm long known as the ureter. Their walls are lined with transitional epithelium surrounded by a layer of muscle fibers and connective tissues. They run downward and open into the urinary bladder.
Urinary Bladder:
It is a large, thin-walled highly muscular pear-shaped sac, composed of transitional epithelium. The muscular layer is well developed and known as the Detrusor muscle. The urinary bladder can be divided into two parts. Its upper part is called a body and it stores the urine while its lower part is called the neck which leads into urethra. At the base of the bladder between the opening of two ureters, there is a triangular area called Trigone or Trigonum Vesical. The neck of the bladder is guarded by two sphincters which contract and relax to pass the urine. The inner sphincter is involuntary and the outer is voluntary. Both sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves innervate the urinary bladder. Urinary bladder can store about 0.5 to 1 liter of urine. Urinary bladder is absent in birds. In both birds and reptiles, the ureters and rectum open into a sac called cloaca which stores both urine and faeces and reabsorbs water from them.
Urethra:
It is a canal which extends from the neck of the bladder to the exterior and its length in male is 20 cm and in the female is 2-4 cm. In the female, it carries only urine and opens into the genital aperture by the urethral orifice. In males, the urethra carries both urine and sperms and opens out at the tip of the penis by the urinogenital aperture. The infection of the urinary tract is more common in women than in a man due to her short urethra.
- Process of digestion in human beings
- Components of Blood
- Human Heart Important Facts
- Nervous System
- Chemical Coordination in Plants & Animals
- Environmental Issues.








Comments (No)