Table of Contents
What is Prism?
A prism is a portion of a transparent medium bounded by two plane faces inclined to each other at a suitable angle. Angle ‘A’ is called the angle of Prism.
Refraction Through Prism:

Let ABC be the principal section of the Prism. Let PQ be the incident ray, QR be the refracted ray and RS be the emergent ray. Let N1O and N2O be the two normals at points Q and R respectively. In the figure, ∠i be the angle of incidence, ∠r1, and ∠r2 be the angles of refraction and ∠e be the angle of emergence. When the emergent ray is produced backward, it meets the incident ray at D. Then ∠EDR is called the angle of deviation (δ).
Calculation of Angle of Deviation:
| From the figure, δ1+ r1 = i ⇒ δ1= (i − r1) …..(i) Also, δ2 + r2 = e ⇒ δ2 = (e − r2) ……(ii) From ΔDQR, δ = δ1 + δ2 ……(1) Put the value of δ1 and δ2 from (i), (ii) in (1), δ = (i − r1) + (e − r2) ⇒ δ = i − r1 + e − r2 ⇒ δ = (i + e) – (r1 + r2) ……(2) From quad. AQOR, A + O = 180° ……(iii) From ΔOQR, O + r1 + r2 = 180° ……(iv) From (iii) and (iv), we have A + O = O + r1 + r2 ⇒ A = r1 + r2 ……(3) Put the value of (r1 + r2) from (3) in (2), δ = (i + e) – A A + δ = i + e If μ be the refractive index of the material of Prism and angles are small. μ = sin i/sin r1 = i/r1 ⇒ i = μr1 and μ = sin e/sin r2 = e/r2 and ⇒ e = μr2 Put these values of i and e in equation (4), ⇒ A + δ = μr1 + μr2 ⇒ A + δ = μ (r1 + r2) ⇒ A + δ = μA [∴ r1 + r2 = A] ⇒ δ = μA – A ⇒ δ = (μ – 1) A ……(5) This is the required expression for the angle of deviation in the case of Prism. |
Derivation of Prism Formula:
The variation of the angle of deviation with the angle of incidence is shown in the figure. From the graph, when i increases, δ decreases first, reaches a minimum, and then δ increases.
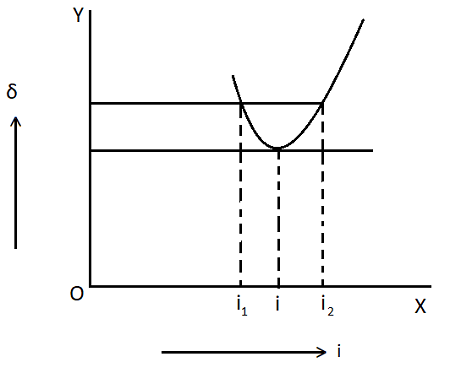
From the graph, we conclude that there is one and only one angle of incidence, for which deviation produced by the prism is minimum.
| In the minimum deviation position, δ = δm ∠ i = ∠ e ∠ r1 = ∠ r2 = ∠ r ……(6) Put (6) in (3), A = r + r ⇒ A = 2r ⇒ r = A/2 ……(7) Put (6) in (4), A + δm = i + 1 ⇒ A + δm = 2i ⇒ i = (A + δm)/2 ……(8) According to Snell’s Law, μ = sin i/ sin r ……(9) Put (7) and (8) in (9), and we have μ = sin [(A + δm)/2] / sin (A/2) ……(10) Equation (10) is the required expression for the Prism formula. |








Comments (No)