Table of Contents
Structure of Human Ear:
The human ear is divided into three main parts the external ear, the middle ear and the internal ear. The first two parts are mainly concerned with hearing whereas the last part is concerned with hearing as well as for maintaining equilibrium and posture of the body.
External Ear:
The external ear consists of the pinna, external auditory meatus and eardrum. The pinna is a flap of elastic cartilage covered by skin. It collects the sound waves. The external auditory meatus is a curved tube that extends up to the tympanic membrane [the ear drum]. The tympanic membrane is composed of connective tissues covered with skin outside and with mucus membrane inside. There are very fine hairs and wax producing sebaceous glands called ceruminous glands in the external auditory meatus. The combination of hair and ear wax [cerumen] helps in preventing dust and foreign particles from entering the ear.
Middle Ear:
It is formed of an irregular, air-filled tympanic cavity. The tympanic cavity is connected to the pharynx by a tubular canal called the eustachian or pharyngo-tympanic canal. Its primary function is to equalize pressure on either side of the eardrum. It contains three ear ossicles– malleus, incus and stapes that link the eardrum with the inner ear through an oval opening known as the fenestra vestibule. The ear ossicles help in passing the vibrations from the eardrum to the internal ear and also to increase the force of vibrations. Directly below the oval window is another opening, the round window.
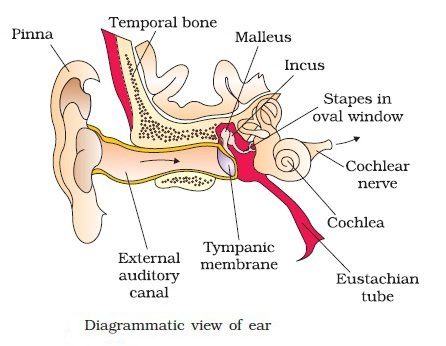
Internal Ear:
It is irregular endolymph filled organ called a membranous labyrinth that occurs inside perilymph filled cavity called the bony labyrinth. The membranous labyrinth is formed of vestibular apparatus and cochlea.
Vestibular Apparatus- consists of membranous semicircular canals, utriculus and sacculus. Semicircular canals are three in number and are ‘C’ shaped fluid-filled loops. They are oriented in a different plane, at right angles to the other two, pointing up-down, side-side and front back. One detects up and down motion, another lateral motion and third forward motion. The ends of semicircular canals are swollen called the ampulla. Inside it is a jelly-like lump, the crista. Semicircular canals open into the utriculus and later into the sacculus by a duct and in turn, the sacculus communicates with the cochlea. Each utricle and saccule has a small thickened region called macule containing hair cells embedded in a jelly-like membrane. Inside the membrane, chalky granules are found called otoliths. These granules crystals respond to the pull of gravity to any movement of the head and thus, maintain the equilibrium of the body. The vestibular apparatus is filled with endolymph.
Cochlear Duct- It is also called lagena. It is spirally coiled like a snail’s shell and is surrounded by a similar shaped bony part, called the cochlear canal, of the bony labyrinth. Both are collectively called the cochlea. In man, cochlea makes about two and three quarter turns. The Wall of the cochlear duct is fused with cochlear bone on the sides to form three chambers-
- Upper- scala vestibuli.
- Middle- scala media (actual cochlear duct).
- Lowers- scala tympani.
The floor of scala media is called basilar membrane whereas its roof is called Reissner’s membrane. The two membranes separate the scala tympani and scala vestibule. Both the scala vestibule and scala tympani canals contain perilymph, a fluid similar to cerebrospinal fluid. The scale media is filled with endolymph, a fluid similar to intracellular fluid and carries a row of sensory hair cell- an organ of Corti located on the basilar membrane. The organ of Corti is sensitive to sound vibrations and conducts the sound stimuli (nerve impulses) to the appropriate part of the brain by the auditory nerve. The auditory nerve branches over the vestibular apparatus and the cochlea.









Comments (No)