Table of Contents
Virus and its Structure:
What is a Virus?
- The term virus was coined by Pasteur in 1880.
- The name virus means venom or poisonous fluid.
- Viruses are a link between the living and the non-living worlds. They show the characteristics of living and non-living both.
- A virus is an ultramicroscopic nucleoprotein entity that becomes active only inside a living cell using the latter’s machinery for multiplication through a separate synthesis of its parts.
- The study of viruses is called virology.
- Viruses cause diseases like smallpox, influenza, herpes, AIDS, poliomyelitis and mumps etc. in humans. Plant diseases like a mosaic, leaf rolling and curling, yellowing and vein clearing, stunted growth, dwarfing etc. may also be viral.
Occurrence of Virus:
A virus is an obligate parasite. It cannot be grown on an artificial culture medium. Viruses are found in living cells of plants, animals and human beings. They are also found in bacterial cells and are called bacteriophages. They were discovered in 1892 by Russian biologist, Iwanovsky, who showed that tobacco mosaic disease in tobacco was caused by microorganisms smaller than bacteria known as viruses. They are extremely small and can pass filter.
On the basis of Host, a Virus is called:
- Zoophage- Animal Virus.
- Phytophage- Plant Virus.
- Bacteriophage- Bacterial Virus.
- Mycophage- Fungal Virus.
- Phycophage- Algal Virus.
- Cyanophage- Blue-green Algal Virus.
- Coliphage- Bacteriophage of colon bacterium Escherichia coli.
Virus Structure:
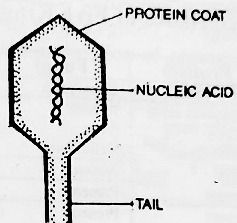
A virus consists of a central core of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protective coat of protein. All plant viruses generally have single-stranded RNA and all animal viruses have either single or double-stranded RNA or double-stranded DNA. Bacterial viruses contain mostly double-stranded DNA. The protein coat protects the nucleic acid, called a capsid and its smaller units are called capsomeres. These capsomeres are arranged in helical or polyhedral geometric forms. It does not carry cytoplasm, nucleus, nucleolus or cell membrane. The nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) is responsible for producing specific characteristics to the virus. It also possesses a long tail for attacking to the bacteria, plants or animals.
Virus resemblance with Living Beings:
- Occur in different varieties or strains.
- They have their own genetic material.
- They can undergo mutations.
- Daughter viruses are genetically similar to parent virus.
- A virus is made of organic molecules.
- They reproduce using the metabolic machinery of the host cell they infect.
- Occasional presence of enzymes.
- They get destroyed by ultraviolet rays.
- It has antigenic property.
Virus resemblance with Non- Living Objects:
- They lack a cellular structure.
- Absence of energy storage mechanism.
- Absence of energy liberation mechanism.
- They can be crystallized and stored in bottles like crystals.
- They do not respire.
- Reproduction does not involve division.
- Inert nature outside living cells.
Since viruses share the properties of both living and non-living, they are rightly said to be the Biologists’s puzzle.
What are the Viroids?
These are the new infectious agents which are smaller than viruses and cause various plant diseases. Each viroid consists of free RNA without surrounded by any nucleoprotein coat. The RNA has low molecular weight and is tightly folded into a circular or linear single-stranded structure.









Comments (No)