Table of Contents
Newton’s Rings Definition:
When a plano-convex lens of a large radius is placed on a plane glass plate, an air film is formed between the lower surface of the lens and the upper surface of the plate. Here the thickness of the film is gradually increased from the point of contact. With the normal incidence of monochromatic light, alternate bright and dark fringes are observed with a dark center. These concentric, circular rings are called Newtons Rings.
Newtons Rings Experimental Set-Up:
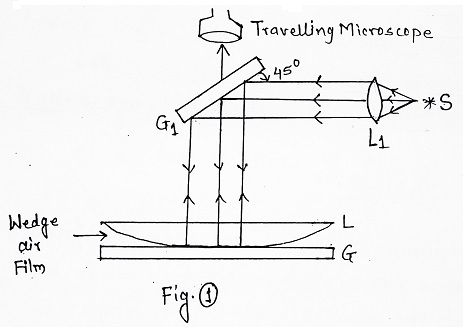
In the above figure, S is a monochromatic source of light; L1 is a focussing lens; G and G1 are plane glass plates; L is a planoconvex lens.
(1) A parallel beam of monochromatic light from source S (through lens L1) is made to fall on a glass plate G1 at 45°.
(2) Light reflected from G1 falls normally on planoconvex lens L kept on optically flat glass plate G.
(3) The light reflected from the lower surface of L and the top surface of G (i.e. from wedge film) have path difference depending on the thickness of air film at the point under consideration.
(4) These superimposed reflected rays are observed by using a travelling microscope in which alternate dark and bright circular rings with the dark center are seen.
(5) Using a travelling microscope diameters of these rings can be determined.
Diameters of Newton’s Dark and Bright Rings:
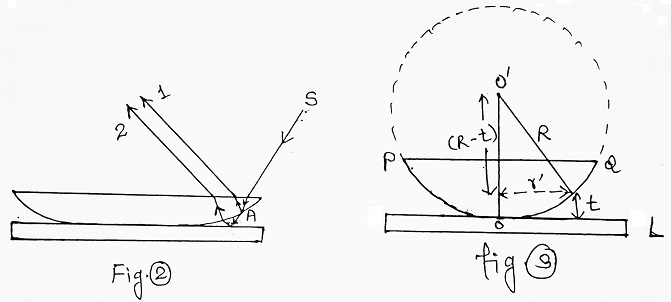
Let SA be a beam of monochromatic light of wavelength λ incident on a film at A is reflected along A1 and simultaneously partly reflected and then reflected by a top surface of the planoconvex lens (ray-2).
| Let R = radius of curvature of lens. µ = Refractive index of film between POQ and L (fig. 3). t = thickness of the film at the point under consideration. r’ = Distance of point under consideration from the point of contact (i.e. the radius of Newton’s ring). |
We know that for a wedge-shaped film the path difference is-
| Path Difference = 2µt cos (r + θ) + λ/2 ……….(i) |
For µ = 1, normal incidence (r = 0) and small θ (cos θ → θ), we have-
| Path Difference = 2t + λ/2 ……….(ii) |
From figure (iii), we have-
| R2 = r’2 + (R – t)2 ⇒ R2 = r’2 + R2 -2Rt + t2 or r’2 = 2Rt – t2 ……….(iii) But R >> t ⇒ r’2 = 2Rt or 2t = r’2/R ……….(iv) ∴ Equation (ii) becomes, r’2/R + λ/2 = Path Difference ……….(v) |
For Dark Ring:
| Path Difference = r’2/R + λ/2 = (2n + 1) λ/2 or r’2/R = nλ, n = 0, 1, 2,……. If Dn is the diameter of the nth dark ring, we can write- Dn = 2r’ ⇒ r’2 = (D2n)/4 ∴ The above equation becomes, D2n/4R = nλ or D2n = 4nRλ ……….(vi) or Dn = √(4nRλ) ⇒ Dn ∝ √n ……….(vii) Thus the diameter of dark rings is proportional to the square root of natural numbers. |
For Bright Ring:
| Path Difference = r’2/R + λ/2 = nλ ⇒ r’2/R = (2n – 1) λ/2 Thus if Dn is the diameter of the bright ring then- D2n = 4r’2 ⇒ D2n/4R = (2n – 1) λ/2 i.e. D2n = (2n -1) 2Rλ ⇒ Dn = √(2Rλ) √(2n – 1) or Dn ∝ √(2n – 1) ……….(viii) Thus the diameter of bright rings is proportional to odd natural numbers. |
Applications of Newton’s Rings:
(1) Determination of Wavelength (λ) or Radius of the Lens (R):
If Dn is the diameter of the nth dark ring, then-
| D2n = 4nRλ |
Similarly, for the mth dark ring, we can write-
| D2m = 4mRλ |
| ∴ D2m – D2n = 4 (m – n) Rλ or λ = (D2m – D2n)/4 (m – n) R |
Thus by knowing the diameters of nth and mth dark rings with a travelling microscope, λ (or R) can be calculated.
(2) Determination of Refractive Index of Liquid (µ):
Let ‘µ’ be the refractive index of a transparent liquid which is placed between lens L and plate P of Newton’s rings apparatus.
| Here the path difference is = 2µt + λ/2 ……….(i) and also 2t = r’2/R ……….(ii) (w.r.t. fig. (3)) ∴ For the nth dark ring, we have- µr’2/R + λ/2 = (2n + 1) λ/2 ⇒ µr’2/R = nλ or µD2n/4R = nλ ⇒ D2n = 4nRλ/µ ……….(iii) Similarly, D2m = 4mRλ/µ ……….(iv) Thus, D2m – D2n = 4(m – n)Rλ/µ ∴ We can write- µliq. = 4(m – n)Rλ/[D2m – D2n]liq. ……….(v) Also for air film- µair = 1 = 4(m – n)Rλ/[D2m – D2n]air ……….(vi) |
Thus from equations (v) and (vi), we get-
| µliq./µair = [D2m – D2n]air/[D2m – D2n]liq. ……….(vii) |
Thus by knowing the diameters of nth and mth rings in the air and then in the liquid film, the refractive index of liquid can be determined.









Comments (No)