Wireless Networking:
Wireless Networking facilitates data transmission through the earth’s atmosphere (air, water, or vacuum) at a much faster rate and provides wide area coverage. Some commonly used technologies for wireless data transmission include microwave, satellite, infrared, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi.
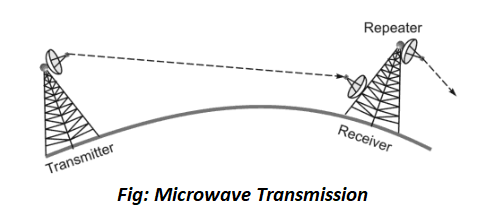
(1) Microwave Transmission- Microwaves are a higher frequency version of radio waves whose transmissions unlike those of the radio, can be focused in a single direction. Microwave transmissions use a pair of parabolic antennae (satellite TV dish antennas) that produce and receive narrow, but highly directional signals. To be sensitive to signals, both the transmitting and receiving antennas must focus within a narrow area. Because of this, both the transmitting and receiving antennas must be carefully adjusted to align the transmitted signal to the receiver. Microwave communication has two forms: terrestrial when it is near the ground and satellite microwave.
(2) Communication Satellite- In satellite communication, signal transferring between the sender and receiver is done with the help of a satellite. In this process, the signal which is basically a beam of modulated microwaves is sent toward the satellite. Then the satellite amplifies the signal and sends it back to the receiver’s antenna present on the earth’s surface. So, all the signal transferring is happening in space. Thus this type of communication is known as space communication.
(3) Infrared Wave Transmission- Infrared frequencies are just below the visible light spectrum. These are the high-frequency waves used for short-range communication. The waves are cheap, directional, and can be easily built; however, the waves do not pass through solid objects. Infrared waves are used in TV remotes, garage doors, wireless speakers, wireless LANs, etc.
(4) Bluetooth- It is a well-defined wireless technology for constructing a mobile ad hoc network. It can be exploited on small scales to build ad hoc WPANs, that is, networks that connect devices such as mobile phones with hands-free headsets, PCs with printers, etc., placed inside a space confined with a circle of ten meters radius. It uses radio signals which are omnidirectional, that is, signals travel in all directions from the source. Hence, the communicating devices need not be aligned with each other. The main feature of Bluetooth is its low power requirements which makes it suitable for handheld devices like cell phones, PDAs, etc. Today, almost all small handheld devices are Bluetooth-enabled. However, the maximum data transmission rate that it supports is only one megabit per second, which makes it unsuitable for exchanging large files or folders. The Bluetooth market focuses on professional and field workers, who need to travel offsite but still require access to corporate communication and information.
(5) W-Fi- The term Wi-Fi which stands for Wireless Fidelity is widely used for creating wireless LANs and also for providing wireless Internet access. To create a wireless LAN, the devices in the network such as laptops, computers, PDAs, etc., should be equipped with wireless network interface cards to send and receive Wi-Fi signals. Wi-Fi technology gives us much freedom of getting connected without any physical preclusion. It makes networking much simple and easy, reliable. For example, the user of Wi-Fi networks can connect to the internet anywhere under Wi-Fi coverage. Besides that, it makes transmitting data faster compared to other types of wireless technologies. One of the disadvantages of a Wi-Fi network is that weak security causes the wireless network vulnerable to attack from intruders. Wi-Fi signals are not confined to the boundaries of the building (in which the wireless LAN is operating), thus any intruder can easily gain access to the network by standing outside the building. Another disadvantage of a Wi-Fi network is its susceptibility to interference from other devices operating in the same area such as wireless phones, other wireless networks, etc.









Comments (No)