Table of Contents
Digestive System of Earthworm:
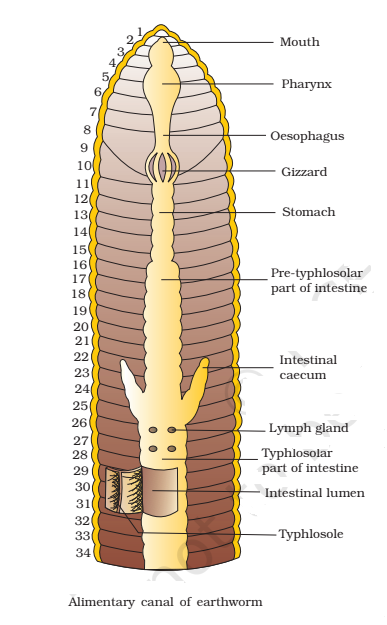
The digestive system of the earthworm consists of the alimentary canal and the digestive glands.
Alimentary Canal:
The alimentary canal is a straight tube and runs between the first to the last segment of the body.
- Mouth and Buccal Cavity- The mouth is a crescentic aperture lying below the prostomium. The mouth leads into a short, thin-walled tube called a buccal chamber or buccal cavity running up to the 3rd segment.
- Pharynx- A pear-shaped muscular pharynx in 3rd and 4th segments with a roof containing a pharyngeal mass/bulb with some chromophil cells. The pharynx is divisible into a dorsal salivary chamber for partial protein digestion (by glands of pharyngeal mass) and a ventral conducting chamber.
- Oesophagus and Gizzard- A small narrow tube, oesophagus lies in the 5th segment and continues into a muscular gizzard in the 6th segment. The gizzard helps in the grinding of food.
- Stomach- The stomach extends from 9-14 segments with a sphincter at either end for the temporary storage of food. The food of the earthworm is decaying leaves and organic matter mixed with soil. Calciferous glands, present in the stomach, neutralise the humic acid present in the humus. Some proteolytic enzymes may also be secreted.
- Intestine- Beyond the stomach, the alimentary canal is called the intestine. It is a long, wide and thin-walled tube extending from the 15th segment up to the anus. The lining of the intestine has ciliated and glandular cells. The intestinal lining is folded to form villi. One of these villi becomes larger and well developed than the others to form the typhlosole. The typhlosole, thus, hangs in the lumen of the intestine and runs mid-dorsally from the 26th segment up to the last except posterior 24, 25 segments. The typhlosole divides the intestine into three regions- pre-typhlosolar, typhlosolar and post-typhlosolar. The pre-typhlosolar region extends between 15-26 segments. Two conical outgrowths or intestinal caeca open in the 26th segment. They reach up to the 22nd segment. The caeca may secrete various digestive enzymes like amylase, lipase, cellulase, chitinase, invertase etc. Typhlosolar region of the intestine is spread from the 27th segment to 75th/95th segment (except last 25). This region is provided with an internal median fold of the dorsal wall of the intestine called the typhlosole, which is in fact, a well developed intestinal villi. The typhlosole increases the absorptive surface of the intestine. The post-typhlosolar part of the intestine occurs in the last 25th segments. Here, the undigested part of food is stored and solidified for passing out as worm castings through the anus.
Digestive glands:
The pharyngeal or salivary gland cells, glandular cells of the stomach, intestine and the intestinal caeca are supposed to be the various digestive glands that secrete the digestive enzymes for digestion of food.
Process of Digestion in Earthworm:
The food of earthworm consists of organic matter, fallen decaying leaves, algae, eggs and larvae of other animals etc. Food is swallowed along with soil by sucking action of the powerful pharynx. The enlargement of the pharyngeal cavity draws the food into the buccal cavity. Digestion is extracellular. In the pharynx, the food is mixed with mucin and proteolytic enzyme secreted by the salivary gland. Mucin secretion lubricates the food and proteolytic enzymes convert proteins into peptones. The oesophagus passes the food into the gizzard. The food is grinded by the contractions of its muscular wall. Finely divided food is mixed with a proteolytic enzyme in the stomach, which digests more proteins. Calciferous glands in the stomach neutralise the humic acid. The digestion is completed in the intestine where proteolytic enzyme converts protein into peptones, diastase converts starch into sugar, lipase splits fat into fatty acid and glycerol and invertin acts on sugar to digest it. The absorption of digested food (amino acid, sugars, fatty acid and glycerol etc.) takes place by diffusion into the intestinal membrane and are utilized for energy and cell synthesis. In the muscular fold, the typhlosole of the intestine increases its absorptive surface and blood distributes the food to all the parts of the body. The undigested particles along with earth are passed out through the anus, as worm castings or vermicasts.








Comments (No)