Math Modules in Python:
| We can use the PyCharm code editor for this example. If you do not know about it then follow this link- How to install PyCharm for Python and create a program in it. |
(1) ceil()– The method ceil() returns the smallest whole number greater than or equal to x.
When you pass float values, it changes to integer values.
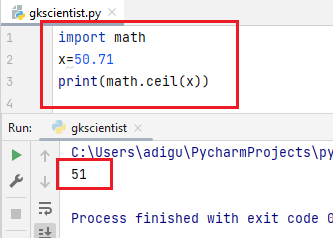
When you pass integer values, no changes take place.
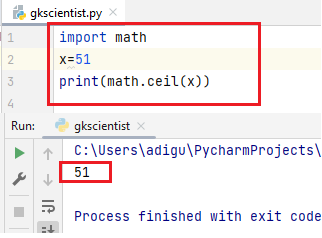
(2) floor()– The floor() function returns the largest whole number less than or equal to x.
When you pass float values, it changes to integer values.
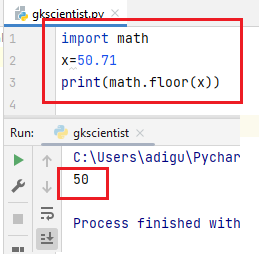
When you pass integer values, no changes take place.
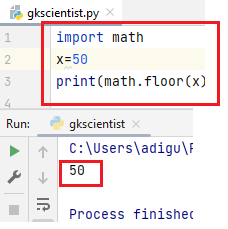
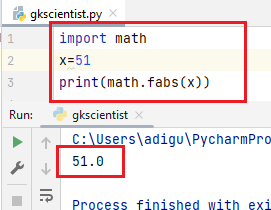
(3) fabs()– The fabs() function returns the absolute value of the x.
Negative values change to positive.
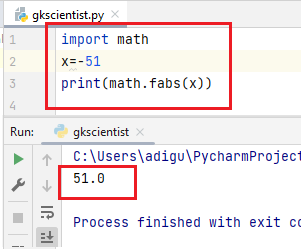
Positive values remain positive.
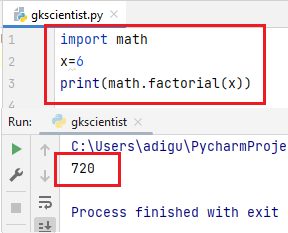
(4) factorial()– The factorial() function return the x factorial as an integer. If you use float or negative value it gives you an error.
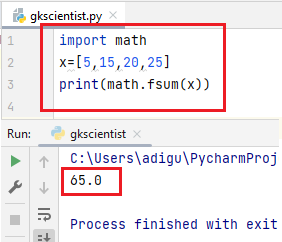
(5) fsum()– The fsum() function returns an accurate floating point sum of values in the iterable.
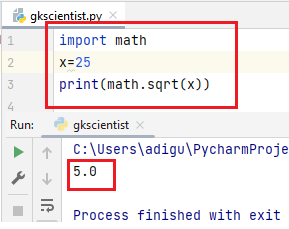
(6) sqrt()– The sqrt() function returns the non-negative square root of x. If x is negative, a domain error occurs.
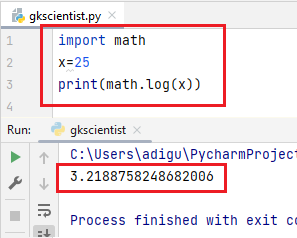
(7) log()– The log() function returns the natural logarithm of x. If x is negative, a domain error occurs. If x is zero, a range error may occur.








Comments (No)