Personal Pronouns:
(1) Personal Pronouns stand for three persons; First Person or the person speaking (I, my, me, we, our, us); Second person or the person spoken to (thou, thy, thee, you, your); Third person or the person spoken of (he, his, him, she, her, it, its, they, their, them).
Different Forms of the Personal Pronouns:
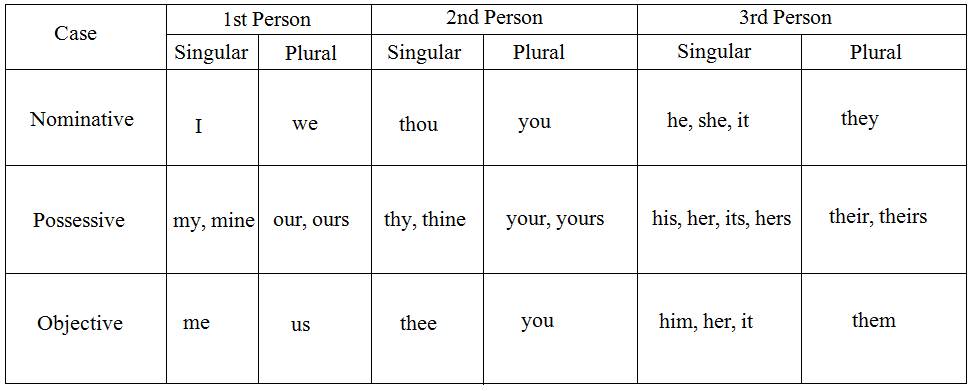
(2) The possessive forms mine, ours, thine, yours, hers, theirs are used when the Noun denoting the thing possessed is understood; as,
- Here is my hat, but where is yours?
- This house is mine and that is theirs.
Note: (a) The possessive forms ours, yours, hers, its, theirs etc., do not take apostrophe ( ‘ ).
| Incorrect | Correct |
|---|---|
| Their’s, her’s, it’s, your’s. | Theirs, hers, its yours. |
(b) There is only one pronoun which needs apostrophe ( ‘ ) forming the possessive and that is one; as,
| Incorrect | Correct |
|---|---|
| One must do his duty. | One must do one’s duty. |
(3) The Pronoun ‘I’ is always written with a capital letter.
Note: It’s = It is. Yes, it’s (it is) correct.
(4) The Pronouns- thou, thy, thine are used in addressing God or in poetry, but not in everyday prose. Instead of these you, your and yours are used both for the singular and the plural nouns; as,
- Strange are thy ways, O God.
- And thou, O Lord, art more than they.
Thou, is also used to express contempt or show familiarity; as,
- Thou rogue, I do not like to see thee.
Note: You is used for both the singular and the plural and always takes a plural verb.
(5) Personal Pronoun ‘We’ is used instead of ‘I’ by editors, authors, kings, spokesmen, etc.; as,
- We (Queen Elizabeth) declare the Parliament open.
- We (the editor of a paper) request the Government to remove the export duty on foodgrains.
Note: An editor, a spokesman, etc. cannot write we in his personal capacity.
| Incorrect | Correct |
|---|---|
| We (an editor) are blessed with a son. | I am blessed with a son. |
(6) Pronoun ‘It’ is used for the following:
(a) Animals young children and lifeless things; as,
- The baby is crying.
- Please silence it.
- The cat loves its kitten.
(b) To emphasis some Noun or Pronoun following it; as,
- It is Hamid who is in the wrong.
(c) To introduce a sentence when it refers to a clause or phrase coming after it or going before it; as,
- It is our duty to respect our parents.
(d) In exclamatory sentences; as,
- What a beautiful scene it is!
(e) In interrogative sentences; as,
- Who was it? It was Sita.
(f) As a sort of object to avoid repetition; as,
- Let us fight it ( the fight) out.
(7) The complement of the verb ‘to be’ (is, am, are, was, were, will be, etc.) is always in the nominative case; as,
- It is I (not me) who have done this.
- It is he (not him) who has done this.
- If I were he (not him), I should have done it.
- That could not be she (not her).
- Who is there? I (not me).
(8) If Pronouns of different persons occur together in the same sentences the Second Person should be placed first, the Third Person next, and the First Person last of all; as,
- You, he and I will go to the cinema.
- You, they and I will go the cinema.
- He and I will go, You and he will go.
Note: In confessing a fault, the Pronoun of the First Person is placed first; as,
- I and you stole mangoes.
- We and he came late.
(9) If a Pronoun refers to more than one Noun or Pronoun of different persons, it must be of the First Person plural in preference to the Second Person, and of the Second Person in preference to the Third Person; as,
- You, he and I must do our duty.
- You and he must do your duty.
(10) When a Pronoun is an object of a Verb or a Preposition it must be in the objective case; as,
- Between you and me (not I) he is a fool.
- Let you and him (not he) do this work.
- May Sohan and I (not me) go out for a walk (I is in the nominative and not the objective case).
- Nobody was present but me (not I).
(11) Sometimes a Pronoun is wrongly used when it is not required; as,
| Incorrect | Correct |
|---|---|
| The student being ill he has not come to school. | The student being ill has not come to school. |
(12) Some Important Distinctions:
- I had no knowledge of you. (knowledge about you.)
- I had not your knowledge. (the knowledge that you had.)
- This is my pen. (one pen.)
- This is a pen of mine. (one of my pens).
- I dislike him smoking. (I dislike the man when, he smokes.)
- I dislike his smoking. (I dislike his action of smoking.)
- We have heard your singing. (how you sing.)
- We have heard you singing. (in the act of singing.)
(13) Some common mistakes with the Personal Pronouns-
| Incorrect | Correct |
|---|---|
| The girl who will stand first she will get a prize. | The girl who will stand first will get a prize. |
| I am not as clever as him. | I am not as clever as he. |
| I am clever than him. | I am clever than he. |
| If I were him, I would have won the bet. | If I were he, I would have won the bet. |
| Have you a pen? I have not got. | Have you a pen? I have not got any. |
| Except he all were present. | Except him all were present. |
| Will you have this book? Thanks, I don’t need. | Will you have this book? Thanks, I don’t need it. |
| Will you take rice? No, I have had. | Will you take rice? No, I have had some. |
| It is you who is to blame. | It is you who are to blame. |
| Your’s sincerely | Yours sincerely. |
| You and he have done his work. | You and he have done your work. |
| He blamed his father and I. | He blamed his father and me. |
| Who is there? It is me. | Who is there? It is I. |









Comments (No)