Table of Contents
What is Rainbow?
A Rainbow is the spectrum of the Sun’s light, in nature. It is a beautiful coloured pattern seen in the sky when the sun shines after the rain.
Conditions For Observing the Rainbow:
Following are the three conditions for observing the Rainbow-
- The observer must stand with his back towards the sun.
- After the rain, the sky should be clear and there is bright sunshine.
- The sun, the observer’s eye and the centre of the arc of the rainbow all should lie in the same straight line.
Types of Rainbow:
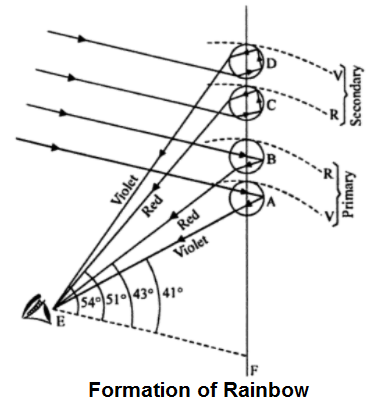
There are two types of Rainbow-
Primary Rainbow:
There are four drops A, B, C, D. From drops A and B the light suffers colours. The main features of Primary Rainbow are as under-
- The red colour is at the outer edge and the violet colour is on the inner edge,
- The violet rays make the angle of 41° with the sun rays whereas the red rays make an angle of 43° with sun rays.
- All the colours lie between these two boundaries i.e. within 2°.
Secondary Rainbow:
From drops C and D, the light suffers two total internal reflections. From drop C, we receive the least deviated red rays and from drop D, we observe the least deviated violet ray. The other colours are obtained in between these two colours. The main features of the secondary rainbow are as under-
- The outer edge is violet and the inner edge is red.
- The violet rays make an angle of 54° with sunrays whereas the red rays make an angle of 51° with sunrays.
- All other colours lie in between these two boundaries i.e. within 3°.
Note: The colours of the primary rainbow are brighter than the colours of the secondary rainbow.









Comments (No)