Table of Contents
What is Self Induction?
Self-induction can be defined as the phenomenon of production of opposing induced EMF in a coil, as a result of varying current in the coil itself.
Explanation of Self Induction:
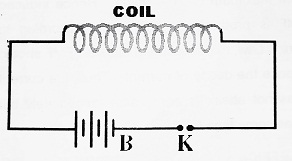
Let us consider a coil connected to a battery B and key K. When key ‘K’ is not pressed, no electric current flows through the coil. Therefore, no magnetic flux is linked with the coil.
When key ‘K’ is pressed, the current in the coil begins to grow from zero to maximum. The magnetic flux linked with the coil also increases from zero to maximum. Hence induced EMF is produced in the coil.
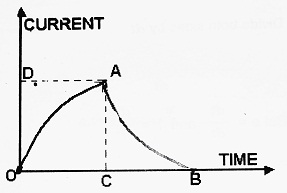
According to Lenz’s Law, the direction of induced EMF should oppose the growth of current (cause) in the coil. Hence the growth of current in the coil is delayed. The growth of current is represented by curve OA in the figure. It is clear that current does not attain its maximum value (OD) immediately but takes some time OC to do so.
When key ‘k’ is released, the current begins to decay from maximum to zero value. The magnetic flux linked with the coil also decreases from maximum to zero value. Hence induced EMF is produced in the coil. According to Lenz’s Law, the direction of induced EMF should oppose the decay of current. Thus, the current does not attain its zero value immediately but takes some time CB to do so.
Co-efficient of Self Induction or Self Inductance:
Let ‘Φ’ be the magnetic flux linked with the coil and let ‘I’ be the current flowing through the coil. It is found that-
| Φ ∝ I ⇒ Φ = LI ……….(i) |
Where ‘L’ is the constant of proportionality and is called a co-efficient of self-induction or self-inductance.
| If I = 1, from (i) ⇒ Φ = L |
Co-efficient of self-induction is numerically equal to the amount of magnetic flux linked with the coil when unit current flows through the coil.
| We know, e = -dΦ/dt ……….(ii) Put the value of ‘Φ’ from (i) in (ii), ⇒ e = -d(LI)/dt ⇒ e = -L . dI/dt ……….(iii) If dI/dt = 1, From (iii), e = -L . 1 ⇒ e = L (numerically) |
Hence co-efficient of self-induction of the coil is equal to induced EMF produced in the coil, when the rate of change of current is unity.
The S.I. unit of co-efficient of self-induction is Henry.
Definition of Henry:
| We have e = -L . dI/dt If dI/dt = 1Amp/sec and e = 1volt ⇒ L = 1Henry (numerically) |
Thus co-efficient of self-induction is said to be 1Henry, when 1 volt EMF is produced in the coil due to one amp/sec rate of change of current in the same coil.
Self Inductance of a Long Solenoid:
As an example, Let us find out the self-inductance of a long air-core solenoid of length l, area of cross-section A and number of turns N. Let the solenoid be a thin one, i.e., the radius of a cross-section is very small compared to length.
If a current I is sent through this solenoid, the magnetic field at axial points inside the solenoid is obtained as-
| B = µ0NI/l |
For a small cross-section, this value of B may be taken almost same everywhere. Thus, the flux through each turn of the solenoid is-
| Φ = B . A = (µ0NI/l) . A |
Net flux linkage with all N turns of the solenoid, i.e., total flux linked with the whole solenoid is-
| NΦ = (µ0N2A/l) . I But NΦ = LI LI = (µ0N2A/l) . I ⇒ L = µ0N2A/l |
This result may be written in terms of a number of turns per unit length.
| n = N/l as L = µ0n2Al |
If a ferromagnetic material of permeability µ is filled inside the solenoid, the self-inductance is greatly increased as then it becomes-
| L’ = µn2Al Since µ is quite large compared to µ0 |
A solenoid or a wire coil of any kind having a definite non-zero value of self-inductance is called an inductor. Any electric wire can never be ideally straight. Even a little curve in the wire will produce a non-zero value of L though it may be very small.









Comments (No)