Table of Contents
Mechanism of a Reaction:
A series of step reactions or elementary reactions proposed to account for the overall reaction is called the mechanism of a reaction. It is not an easy task and requires the experience and indignity of the person. The necessary condition for a reaction mechanism is that it must lead to the correct rate law. It is also known by experiments that in the case of complex reactions, the slowest step determines the rate of reaction. Let us discuss the mechanism of some reactions.
Reaction Involving Two First Order Consecutive Steps:
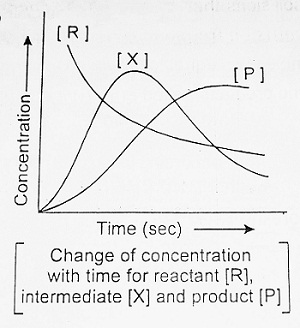
In such reactions, a reaction takes place in two steps both of which are first order, i.e.,
| R ———-> X ……….(i) and X ———-> P ……….(ii) |
Now ‘X’ is produced by step (i) and consumed by step (ii). The intermediate X accumulates and reaches a maximum after which it decays to zero concentration and is converted into a product. However, the concentration of product will always increase. These results are shown above.
Reaction Involving Slow Step:
If a reaction takes place by a sequence of steps and one of the steps is slow, then the rate of the reaction depends on that slow step. Example- Thermal decomposition of N2O5 is written as-
| 2N2O5 ———-> 4NO2 + O2 |
According to rate law, it is found that the rate of reaction = k [N2O5].
In order to explain the above mechanism, it is believed that the above reaction proceeds through the following two steps-
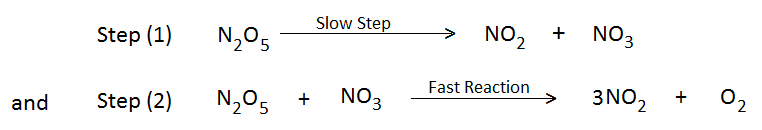
Hence, the above reaction is the unimolecular reaction of the first order as step (1) is the rate-determining step.
Reaction Involving Steady-State Concentration of Intermediate:
In some reactions, the reactants combine to form an intermediate and this intermediate then decompose to form the product. Consequently, the concentration of the intermediate then remains constant over time which is called a steady-state. Therefore, we can assume that the change in concentration with time for these reactive intermediate is zero. This assumption is helpful for driving the rate expression for complex reactions.
Reactions Involving Intermediate in Equilibrium with the Reactants:
Consider a general reaction,
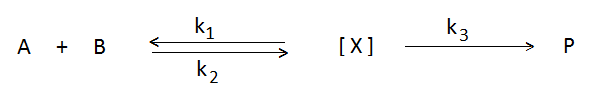
Thus, the rate of reaction is given by the rate of decomposition of the complex.
| Rate of reaction = k3 [ X ] ……….(i) |
By applying the law of chemical equilibrium to reversible step-
| keq = [ x ] / [ A ] [ B ] and keq = k1/k2 ∴ [ x ] = keq [ A ] [ B ] ……….(ii) |
Put equation (ii) in equation (i)-
| Rate of reaction = k3 keq [ A ] [ B ] = k3 (k1/k2) [ A ] [ B ] = k0 [ A ] [ B ] |
Thus, the reaction is of second order and the final rate constant involves all the rate constants of the reaction.







Comments (No)