Roots and Coefficients of a Quadratic Equations:
The roots of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 (a ≠ 0) are given by,
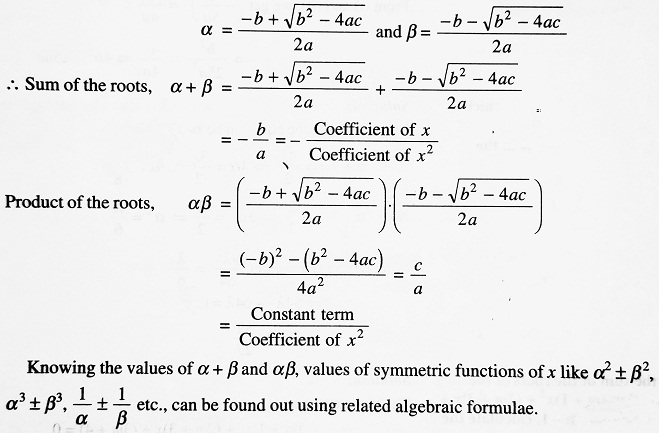
| Example 1- If one of the roots of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 is three times the other, then prove that 3b2 = 16 ac. Solution- The given equation is, ax2 + bx + c = 0 Let α, 3α be its roots. Now, α + 3α = -b/a ⇒ 4α = -b/a ⇒ α = -b/4a …………(i) Also, α . 3α = c/a ⇒ 3α2 = c/a ⇒ α2 = c/3a …………(ii) Substitute the value of α from (i) in (ii)- (-b/4a)2 = c/3a ⇒ b2/16a2 = c/3a ⇒ 3b2 = 16ac |
| Example 2- If αβ are the roots of the equation x2 – 6x + P = 0 such that 3α + 2β = 20, then find the value of P. Solution- The given equation is, x2 – 6x + P = 0 Now, α, and β are their roots. α + β = 6 ……….(i) and αβ = P ……….(ii) Also 3α + 2β = 20 ……….(iii) Solving (i) and (iii)- α + β = 6 3α + 2β = 20 ⇒ α/(20 – 12) = β/(18 – 20) = -1/(2 – 3) ⇒ α/8 = β/(-2) = 1/1 ⇒ α = 8, β = -2 Now from (ii)- αβ = P ⇒ (8) (-2) = P ⇒ P = -16 |
| Example 3- If the difference of the roots of equation x2 + ax + b = 0 be unity then prove that a2 + 4b2 = (1 + 2b)2. Solution- The given equation is, x2 + ax + b = 0 Let its roots be α and β such that α – β = 1 ⇒ √[(α + β)2 – (4αβ)] = 1 ⇒ √[(-a)2 – 4b] = 1 Squaring both sides, we get- ⇒ a2 – 4b = 1 ⇒ a2 = 1 + 4b ⇒ a2 + 4b2 = 1 + 4b + 4b2 ⇒ a2 + 4b2 = (1 + 2b)2 |
| Example 4- If k be the ratio of the roots of equation x2 – ax + b = 0 then prove that (k2 + 1)/k = (a2 – 2b)/b. Solution- The given equation is, x2 – ax + b = 0 Let αk and α be the roots of the equation. Sum of root = -b/a ⇒ αk + α = a ⇒ α (k + 1) = a ⇒ α = a/(k + 1) ……….(i) Product of root = c/a ⇒ αk . α = b ⇒ α2k = b ……….(ii) Substitute (i) in (ii), we get- [a/(k + 1)]2 k = b ⇒ [a2/(k2 + 1 + 2k)] k = b ⇒ a2k = b (k2 + 1 + 2k) ⇒ b (k2 + 1) = a2k – 2bk ⇒ b (k2 + 1) = k (a2 – 2b) ⇒ (k2 + 1)/k = (a2 – 2b)/b |







Comments (No)