Table of Contents
Polar and Non-polar Covalent Bonds:
The mutual sharing of a pair of electrons between two atoms (like atoms and unlike atoms) can lead to the formation of two types of covalent bonds, namely, polar covalent bond and non-polar covalent bond. We shall discuss these two types of covalent bonds.
Polar Covalent Bonds:
When a covalent bond is formed by the mutual sharing of a pair of electrons between two dissimilar atoms (atoms of different elements) having different electronegativities, then bonded electrons are not equally shared between the two atoms. On the other hand, the shared pair of electrons is shifted slightly towards a more electronegative atom. This results in charge separation. As a consequence, the centres of positive and negative charges of the system do not coincide. Thus, one end of the chemical bond acquires a small negative charge while the other end of the bond gets a small positive charge. In other words, the more electronegative atom acquires a little negative charge and the less electronegative atom gets a little positive charge. These charges are usually written as δ+ and δ–. Such a type of chemical bond is referred to as a polar covalent bond or simply a covalent bond having a partial ionic character.
Let us consider a typical instance of hydrogen chloride, HCl. In the formation of hydrogen chloride molecule, HCl, two different atoms namely hydrogen and chlorine share a pair of electrons. Chlorine which is more electronegative than hydrogen attracts the shared pair of electrons to a greater extent as compared with hydrogen. Consequently, the electron density in the chemical bond is more concentrated on the chlorine side of the bond than the hydrogen. This trend results in the accumulation of a slight negative charge (δ-) on the chlorine atom and an equivalent positive charge (δ+) on the hydrogen atom. Hence, HCl may be represented as Hδ+– Clδ-. This type of covalent bond formed between two dissimilar atoms is referred to as a polar covalent bond. The polar covalent bond has a partial ionic character. The compounds containing polar covalent bonds are referred to as polar covalent compounds.
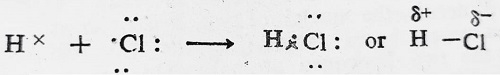
Similarly, hydrogen fluoride, HF, is another instance of polar covalent molecule.
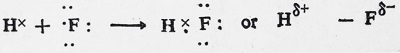
Water and ammonia afford other instances of polar molecules containing more than one polar covalent bond.
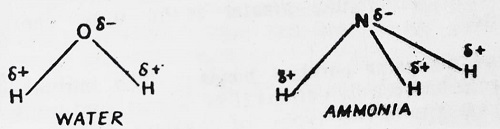
The partial polar or ionic character of a covalent bond is determined by the difference in the electronegativity values of the two participating atoms. Greater is the difference in the electronegativity values of the two atoms, greater is the polarity (partial ionic character) of the molecule formed. As a matter of fact, nearly all the covalent bonds between the unlike atoms are polar or partially ionic in character.
Non-polar Covalent Bonds:
When a covalent bond is formed by the mutual sharing of a pair of electrons between two similar atoms (atoms of the same element) or two dissimilar atoms having a very slight difference in their electronegativity values, then the bonded electrons are evenly distributed around the nuclei of the two atoms. As a result, the bond so formed is referred to as a non-polar covalent molecule. The resulting molecule is known as a non-polar covalent molecule. An essential characteristic of a non-polar covalent bond is that the centre of the positive charge of the bonded atoms coincides with the centre of their negative charge.
For instance, take the case of a hydrogen molecule. In the formation of a hydrogen molecule, the nuclei of two hydrogen atoms attract the pair of electrons to an equal extent (i.e. the electron pair is equally shared between the two hydrogen atoms). This gives rise to the formation of a non-polar covalent bond.
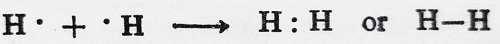
Similarly, two chlorine atoms share one pair of electrons to give rise to the formation of a chlorine molecule. Consequently, the nuclei of the two chlorine atoms have equal attraction for the shared pair of electrons. In other words, the shared pair of electrons will be at equal distances from both the nuclei of two chlorine atoms.










Comments (No)