Table of Contents
Theory of Diffraction Grating:
Plane Diffraction Grating:
An arrangement consisting of a large number of parallel slits of the same width and separated by equal opaque spaces is known as a diffraction grating.
Gratings are constructed by ruling equidistance parallel lines on a transparent plate such as a glass plate, with a fine diamond point. The ruled lines are opaque to light while the space between any two lines is transparent to light and it acts as a slit.
Grating Element (d):
If ‘a’ is the width of each slit and ‘b’ is the width of opaque space, then d = (a + b) is called the grating element which is nothing but the centre-to-centre spacing between any two successive slits.
Example- If there are 15,000 lines ruled per inch (i.e. 2.54 cm), then the grating element is given by-
| d = (1/15,000) inch d = (2.54/15,000) cm |
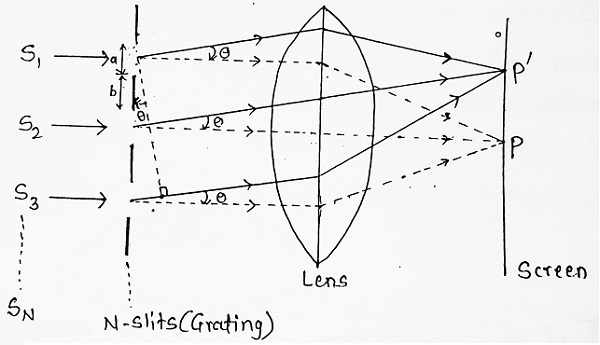
Diffraction at N-slits of Grating:
We know that the resultant amplitude of light diffracted at a single slit through angle ‘θ’ is given by-
| A = A0 sin α/α ……….(i) where, α = (π/λ) d sin θ ……….(ii) |
Let us now consider that there are total ‘N’ parallel slits of grating, then all the secondary wavelets in each slit can be replaced by a single wave of amplitude (A0 sin α/α).
Let there be S1, S2, S3, ………. SN mid-points of N parallel slits. We want to find out the resultant effect due to N-vibrations of N-slits. For N-slits we can take use of an amplitude-phase diagram.
If ‘θ’ is the angle of diffraction, then the path difference between rays diffracted from two adjacent slits is-
| Path Difference = (a + b) sin θ ……….(iii) and ∴ Phase Difference = (2π/λ) (a + b) sin θ ……….(iv) |
Hence to find out the resultant amplitude of P’, we have to find out the resultant of N-vibrations of equal amplitude (A0 sin α/α), equal periods and constant phase difference (2π/λ) (a + b) sin θ.
| Let (2π/λ) (a + b) sin θ = 2β, say ……….(v) |
Then by vector addition method, the resultant amplitude of N-waves is given by-
| A = (A0 sin α/α) (sin Nβ/sin β) ……….(vi) |
and the corresponding resultant intensity at P’ is given by-
| I ∝ A2 or I = (A02 sin2 α/α2) (sin2 Nβ/sin2 β) I = I0 (sin α/α)2 (sin2 Nβ/sin2 β) ……….(vii) |
Here the factor I0 (sin α/α)2 gives intensity distribution in diffraction pattern due to a single slit and (sin2 Nβ/sin2 β) gives intensity distribution due to N-slits.
Conditions of Maxima and Minima:
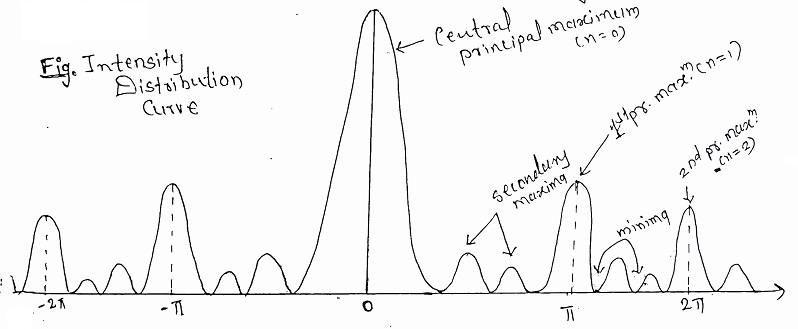
| Case I- Principal Maxima: The resultant intensity at P’ is given by- I = I0 (sin α/α)2 (sin2 Nβ/sin2 β) Intensity is maximum when sin β = 0 ⇒ β = ± nπ i.e. (π/λ) (a + b) sin θ = ± nπ or (a + b) sin θ = ± nλ ……….(viii) The above equation is also called as “grating law” in which n = 0, 1, 2, 3, —— is an order of diffraction. And for n = 0, the position is called the central principal maximum. n = 1, it is called 1st principal maximum. n = 2, 2nd principal maximum and so on. |
| Case II- Minima: Intensity is minimum when sin Nβ = 0, but sin β ≠ 0. ∴ Nβ = ± mπ, where, β = (π/λ) (a + b) sin θ i.e. β = (π/λ) (a + b) sin θ = ± mπ/N or (a + b) sin θ = ± mλ/N ……….(ix) Where ‘m’ can have all integral values except 0, N, 2N, …….., nN, because for these values we get principal maxima. |
| Case III- Secondary Maxima: In between two minima, which are located between two adjacent principal maxima, the secondary maxima are observed. |








Comments (No)