Table of Contents
Improper Fractions: Converting And Calculating with Ease
Fractions are the necessary mathematical fundamentals that need to be understood to perform various types of calculations.
A fraction helps to show the part of a whole thing. The numerator and denominator are numbers that describe how a part relates to a whole.
To solve the fraction, you may do it manually, but if you need a convenient way to solve it, you can get the assistance of a fraction calculator, To perform all the arithmetic operations on the given fractions, go to Fraction Calculator and take advantage of the free online calculator.
Various types of fractions are:
- Proper Fractions.
- Improper Fractions.
- Mixed Numbers or Mixed Fractions.
What Are Improper Fractions?
If x > y, then x/y is an improper fraction. For example: 6/5, and 7/3 are improper fractions because the numerator is greater than the denominator.
Examples of Improper Fractions are:
- 20/3
- 11/5
- 17/4
- 19/3
- 7/2
How To Simplify Improper Fractions?
Follow the below-mentioned steps:
- Check whether the given fraction is an improper fraction or not.
- Determine how many parts the numerator is divided by the denominator.
- Check the common factor.
- Now cancel the same terms.
The following result will be the simplified fraction. Check out the following example for better understanding:
| Example: Simplify the fraction 20/8 Solution: As we can see 20>8 so it’s an improper fraction Now factorize both the numerator and denominator: 20 = 2 x 2 x 5 8 = 2 x 2 x 2 Here 2 is the common factor so cancel them 5/2 The convenient way to simplify and convert fractions to mixed numbers is through the fraction calculator. It just requires input and provides you with a step-by-step solution. |
Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers:
You need to divide the denominator by the numerator in order to convert an improper fraction into a mixed number, After doing so you will get a whole number as the quotient, where the remainder is the numerator and the divisor is the denominator.
| Example: Convert 19/4 to a mixed fraction Solution: Divide 19 by 4 The quotient will be 4 and the remainder will be 3 So the mixed fraction will be: 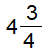 |
Mixed To Improper Fraction: Suppose there is a mixed fraction 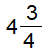 , now convert it into an improper fraction. , now convert it into an improper fraction.Solution: Multiply 4 by 4 4 x 4 = 16 Now add 3 16 +3 = 19 Thus the required numerator of the improper fraction is 19 while the denominator remains the same. Therefore, the resultant improper fractions is 19/4. |
Addition of Improper Fractions:
Two scenarios need to be considered while performing the addition on improper fractions that are:
| (1) If the denominators are the same, then the addition will be done as below: 17/4 + 19/4 = (17 + 19)/4 = 36/4 (2) If the denominators are different, then the addition of improper fraction will be done as: 17/4 + 19/5 Determine the least common multiple for both fractions. In this case, the least common multiple is 20. Now multiply the numerators with the dividend of 20 and add them. 17/4 + 19/5 = (85 + 76)/20 = 161/20 Also, you can get the assistance of the adding fractions calculator to perform the addition effortlessly. |
Subtraction of Improper Fractions:
The process is similar to the addition of the improper fractions.
| (1) If the denominator is the same, then just subtract the numerators as below: 9/3 – 5/3 = (9-5)/3 = 4/3 (2) If denominators are not the same, then find the least common multiple and multiply the numerators with the dividends of the least common multiple. After that perform the subtraction as we have done below: 9/8 – 5/2 = (9-20)/8= -11/8 |
Final Words:
Fraction calculators enable users to perform different arithmetic operations on improper fractions with ease. They not only develop problem-solving skills but also save time which can be invested in understanding mathematical principles.







Comments (No)