
Central Teacher Eligibility Test: CTET December 2018 Question Paper with Answers [Paper- I Main]
- Which one of the following statements is true about the role of heredity and environment?
(1) Certain aspects of development are influenced more by heredity and others more by environment.
(2) A child’s ability to learn and perform is completely decided by the genes.
(3) Good care and a nutritious diet can fight off any disorder a child is born with.
(4) Environment plays a significant role only in the child’s language development.
Ans: (1) Certain aspects of development are influenced more by heredity and others more by environment.
- Which one of the following statements cannot be attributed to Piaget’s theory?
(1) Development occurs in qualitative stages.
(2) Children construct and use knowledge about their world.
(3) Learning takes place through constant practice.
(4) Children act on their environment.
Ans: (3) Learning takes place through constant practice.
- Which one of the following is not a limitation of the preoperational thought?
(1) Tendency to concentrate
(2) Development of the symbolic thought
(3) Egocentrism
(4) Irreversibility
Ans: (2) Development of the symbolic thought.
- Play has a significant role in development of young children for the following reasons, except—
(1) they gain mastery over their body
(2) it stimulates their senses
(3) it is just a pleasant way to spend time
(4) they acquire new skills and learn when to use them
Ans: (3) it is just a pleasant way to spend time.
- Which one of the following questions invites children to think critically?
(1) Do you know the answer to this?
(2) What is the right answer?
(3) Can you think of a similar situation?
(4) What are the different ways in which we can solve this?
Ans: (4) What are the different ways in which we can solve this?
- Which one of the following options best describes progressive
education?
(1) Learning by doing, project method, cooperative learning
(2) Thematic units, regular unit tests, ranking
(3) Personalized learning, ability grouping, labeling students
(4) Project method, ability grouping, ranking
Ans: (1) Learning by doing, project method, cooperative learning.
- Which one of the following statements about progressive education explains—Education is life itself ?
(1) School education should continue as long as possible.
(2) Schools are not required, children can learn from their life
experiences.
(3) Education in schools should reflect the social and natural
world.
(4) Life is the true educator.
Ans: (3) Education in schools should reflect the social and natural
world.
- Which one of the following can be considered as a contribution of
Kohlberg’s theory?
(1) His theory has supported an association between cognitive maturity and moral maturity.
(2) The theory has elaborate testing procedures.
(3) It establishes a clear relationship between moral reasoning and action.
(4) His belief is that children are moral philosophers.
Ans: (1) His theory has supported an association between cognitive maturity and moral maturity.
- The Zone of Proximal Development refers to—
(1) the phase when maximum development is possible
(2) the developmental phase when child takes complete responsibility for learning
(3) a context in which children can almost perform a task on their
own with the right level of support
(4) the point in learning when support can be withdrawn
Ans: (3) a context in which children can almost perform a task on their
own with the right level of support.
- An androgynous personality—
(1) refers to men with feminine traits
(2) has a balance of what are generally considered masculine and feminine traits
(3) tends to be assertive and arrogant
(4) adheres to stereotypical gender roles prevalent in the society
Ans: (2) has a balance of what are generally considered masculine and feminine traits.
- Children acquire gender roles through all of the following, except—
(1) media
(2) socialization
(3) culture
(4) tutoring
Ans: (4) tutoring.
- One of the critiques of standardized tests has been that—
(1) they represent largely the mainstream culture and are therefore biased
(2) their language is difficult to understand
(3) the tests cannot be administered on large populations
(4) they do not give a clear picture of a child’s ability
Ans: (1) they represent largely the mainstream culture and are therefore biased.
- The theory of multiple intelligence says that—
(1) intelligence can be rapidly accelerated
(2) intelligence can be of several kinds
(3) paper-pencil tests are not helpful
(4) intelligence can be multiplied with effective pedagogy
Ans: (2) intelligence can be of several kinds.
- Teacher can utilize both assessment for learning and assessment of learning to—
(1) know children’s progress and achievement level
(2) know learning needs of child and select teaching strategy accordingly
(3) assess child’s performance at periodic intervals and certify his/her performance
(4) monitor children’s progress and set appropriate goals to fill their learning gaps
Ans: (1) know children’s progress and achievement level.
- Which one of the following is not related to Continuous and Comprehensive Evaluation?
(1) It has been mandated by the Right to Education Act of India.
(2) It is an integral part of teachinglearning process.
(3) It focuses on child’s achievement in different learning areas.
(4) It is useful to label children as slow, poor or intelligent
Ans: (4) It is useful to label children as slow, poor or intelligent.
- Giftedness in children can be attributed to—
(1) an interplay between heredity and environment
(2) a resource-rich environment
(3) successful parents
(4) a disciplined routine
Ans: (1) an interplay between heredity and environment.
- Children coming from socioeconomically disadvantaged backgrounds need a classroom environment which—
(1) teaches them good behaviour
(2) values and uses their cultural and linguistic knowledge
(3) discourages the use of their language so that they learn the mainstream language
(4) categorizes children based on their abilities
Ans: (2) values and uses their cultural and linguistic knowledge.
- The intervention needed for creative and talented children in the classroom rests on—
(1) use of customized and stimulating instructional methods by the teacher
(2) giving extra time to them
(3) being affectionate towards them
(4) giving them the responsibility of teaching other children
Ans: (1) use of customized and stimulating instructional methods by the teacher.
- Which one of the following ways is not a suitable way to help hyperactive children learn?
(1) Breaking up a task into small, manageable segments
(2) Offering alternative ways of learning
(3) Including physical activity in their daily schedule
(4) Reprimanding them often for being restless
Ans: (4) Reprimanding them often for being restless.
- Patterns of divergent thinking identify children, who are—
(1) disabled
(2) dyslexic
(3) creative
(4) resilient
Ans: (3) creative.
- Which one of the following does not describe the ways in which a teacher can model problem solving for children in the classroom?
(1) Discuss your thought processes about solving a particular problem
(2) Be honest about making mistakes while solving something
(3) Use vocabulary like think, ideas, trial and different answers
(4) Ask questions with convergent answers
Ans: (4) Ask questions with convergent answers.
- Which one of the following is an emotion?
(1) Memory
(2) Fear
(3) Attention
(4) Stimulus
Ans: (2) Fear.
- A three-year-old child explains that milk is produced by a machine at the milk booth. Which one of the following offers the best explanation of the child’s understanding?
(1) The child has very limited exposure of the world.
(2) The child’s answer is based on his/her experience of buying milk from the milk booth.
(3) The child has never seen cows.
(4) The child’s family does not offer a stimulating environment to the child.
Ans: (2) The child’s answer is based on his/her experience of buying milk from the milk booth.
- Which one of the following best describes a teacher’s role?
(1) Teacher’s most important role in the classroom is to maintain discipline
(2) A teacher should adhere to the prescribed textbook
(3) Completing the syllabus on time leaving enough time for revision is important
(4) Creating a relaxed space where children learn through dialogue and inquiry
Ans: (4) Creating a relaxed space where children learn through dialogue and inquiry.
- Which one of the following classrooms encourages rich learning?
(1) A classroom with a variety of material displayed in the class beyond the reach of children so that the material lasts longer
(2) A classroom with open activity corners and a variety of children’s literature in open shelves accessible any time of the day
(3) A classroom with neatly organized material in cupboards brought out once a week for free play
(4) A classroom with structured and planned learning driven by textbook content
Ans: (2) A classroom with open activity corners and a variety of children’s literature in open shelves accessible any time of the day.
- Which one of the following best describes the role of textbooks in the
classroom?
(1) They are one of the resource and reference materials available in the class.
(2) They maintain homogeneity in learning across a State or the Nation.
(3) They provide guidance to teachers and parents about the course of study.
(4) They form the most essential learning resource in a resource-starved context.
Ans: (1) They are one of the resource and reference materials available in the class.
- The National Curriculum Framework–2005 derives its understanding from—
(1) humanism
(2) behaviourism
(3) constructivism
(4) cognitive theories
Ans: (3) constructivism.
- The children in a class can be considered to be motivated if—
(1) they come to school neatly dressed in uniform
(2) they maintain discipline in the class
(3) all are regular in attendance
(4) they ask questions seeking clarification from the teacher
Ans: (4) they ask questions seeking clarification from the teacher.
- Which one of the following is the most suitable to improve children’s learning?
(1) Regular assessment test should be conducted.
(2) Teacher should explain the content using different examples and illustrations.
(3) All types of learning material should be there in the class.
(4) Teacher should facilitate children to interact with each other on real-life situations.
Ans: (4) Teacher should facilitate children to interact with each other on real-life situations.
- The discipline which has a significant role in a learning environment is of the kind which helps—
(1) children to regulate and monitor their own learning
(2) to create silence
(3) teachers to give instructions
(4) children rote memorize their lessons
Ans: (1) children to regulate and monitor their own learning.
- The assessment of what children learn in mathematics in primary classes should not focus on—
(1) understanding of the mathematical concepts
(2) development of mathematical language
(3) preciseness in answering mathematics problems
(4) development of reasoning skills
Ans: (3) preciseness in answering mathematics problems.
- What sequence of the following instructions should be followed in development of a mathematical concept in elementary classes?
I. Drawing pictures
II. Using symbolic representation
III. Providing experiences
IV. Explaining through language
(1) IV, III, I, II
(2) III, IV, I, II
(3) IV, III, II, I
(4) III, I, II, IV
Ans: (2) III, IV, I, II.
- A child subtracted two numbers as shown below :
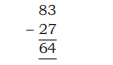
Which one of the following statements gives idea about the child’s learning of subtraction?
(1) The child has misconceptions about place value in the process of subtraction.
(2) The child does not know how to subtract.
(3) The child knows the process of subtraction of two-digit numbers.
(4) It is a mistake and it can be rectified by repeated practice
Ans: (1) The child has misconceptions about place value in the process of subtraction.
- Arrange the following steps of cycle of learning and assessment in order :
I. Teaching-learning integrated with assessment
II. Planning and organization of teaching-learning and assessment
III. Developing progress reports
IV. Reporting and communicating feedback of children’s learning and progress
(1) II, I, III, IV
(2) I, II, IV, III
(3) IV, I, II, III
(4) II, IV, I, III
Ans: (1) II, I, III, IV.
- Why are Roman numerals not commonly used in writing numbers
like the Hindu-Arabic numerals?
(1) The Roman numerals do not employ place value, so calculations are difficult to perform using these numerals.
(2) Roman numerals are difficult to remember.
(3) The formation of numbers using Roman numerals is a complicated task.
(4) Children get confused with the English alphabet and Roman numerals.
Ans: (1) The Roman numerals do not employ place value, so calculations are difficult to perform using these numerals.
- A teacher encourages the children in her class to explain the physical properties of the objects around them in their own words. What is the most appropriate objective of the teacher to do such an activity with her students?
(1) It is a very interesting activity which can be performed in the free time for revisiting the concept of shapes.
(2) Children enjoy explaining the objects in their own language like they enjoy playing dumb charades.
(3) It makes the children observe the physical properties of an object informally which deepens their understanding about shapes.
(4) It is a useful activity which introduces a child to the shapes.
Ans: (3) It makes the children observe the physical properties of an object informally which deepens their understanding about shapes.
- The mathematics used by illiterate shopkeeper—
(1) is not useful in the mathematics classroom
(2) is very useful in solving all mathematical problems
(3) has ambiguity and very low level of correctness in it
(4) should be discussed by the teachers in classrooms as an alternate strategy in solving related problems
Ans: (4) should be discussed by the teachers in classrooms as an alternate strategy in solving related problems.
- How should a teacher handle a heterogeneous group of children in a mathematics classroom?
(1) By grouping the children of same ability together and giving them questions according to their ability
(2) By grouping all children together in the same classroom
(3) By grouping the children of different abilities together so that they can learn from each other
(4) By doing questions according to low ability children in the class and giving the complex questions as home assignments to higher ability children
Ans: (3) By grouping the children of different abilities together so that they can learn from each other.
- The learning outcomes in mathematics are developed—
(1) such that children may be told small steps for calculations
(2) to increase the achievement of children in various educational surveys
(3) to define classwise competencies and skills to be achieved by children
(4) to prepare children for year-end examinations
Ans: (3) to define classwise competencies and skills to be achieved by children
- Which one of the following happenings in the classroom is an activity?
(1) Teacher explaining how to do sums
(2) Children reciting counting in form of rhymes
(3) Children copying from blackboard
(4) Children engaged in exploration
Ans: (4) Children engaged in exploration.
- To develop skill of counting among children, which one of the following is not required to be learned as prenumber concept?
(1) One to one correspondence
(2) Seriation
(3) Reciting number names randomly
(4) Creating groups
Ans: (3) Reciting number names randomly.
- On asking a child ‘‘What is area?’’, he/she answered length × breadth. What can you say about the child’s understanding about the concept
of area?
(1) The child has no idea about the concept of area.
(2) The child used the area of rectangle as general idea of area
of any closed shape.
(3) The child is right in saying area is length × breadth.
(4) The child is confused between the concept of area and perimeter.
Ans: (2) The child used the area of rectangle as general idea of area of any closed shape.
- Which one of the following statements is true with respect to mathematics learning?
(1) Mathematics is a difficult subject to learn.
(2) Generally girls are weaker in mathematics.
(3) Everybody can learn mathematics.
(4) Mathematics can only be learnt by rigorous practice.
Ans: (3) Everybody can learn mathematics.
- To teach the Pythagoras theorem, a teacher has distributed a sheet on which four right-angled triangles were drawn and asks the child to
find the relationship between the sides of a triangle. In the above situation, the teacher used—
(1) inductive method
(2) deductive method
(3) lecture method
(4) laboratory method
Ans: (1) inductive method.
- Which one of the following statements is not true about ‘concept maps’?
(1) Concept maps represent a collection of interconnected concepts and links connecting them.
(2) Concept maps should be constructed by teachers only.
(3) Concept maps are hierarchical in nature.
(4) Concept maps help in linking prior knowledge to new instruction.
Ans: (2) Concept maps should be constructed by teachers only.
46.

Ans: (3).
47.

Ans: (2) One of them is not a parallelogram.
- Which one of the following represents the number ‘eleven thousand eleven hundred eleven’?
(1) 111111
(2) 12111
(3) 11000110011
(4) XIXIXI
Ans: (2) 12111.

Ans: (4) 22000 units.
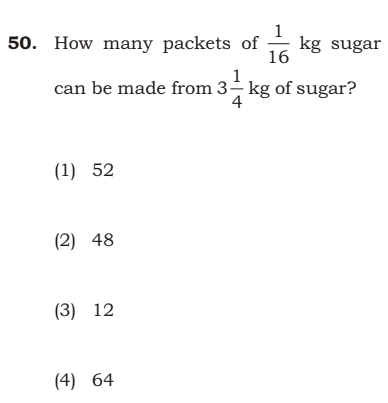
Ans: (1) 52.
- Harish started his journey at 18 : 40 and finished at 22 : 20. The time taken in completing the journey is—
(1) 3 hours 40 minutes
(2) 3 hours 80 minutes
(3) 4 hours 40 minutes
(4) 3 hours 20 minutes
Ans: (1) 3 hours 40 minutes.
- A bucket of capacity 2000 mL is to be filled by using containers measuring 200 mL and 300 mL. Which one of the following combinations of containers is not correct for filling the bucket completely by the containers of 200 mL and 300 mL respectively?
(1) 1, 6
(2) 4, 4
(3) 7, 2
(4) 6, 3
Ans: (4) 6, 3.

Ans: (2).
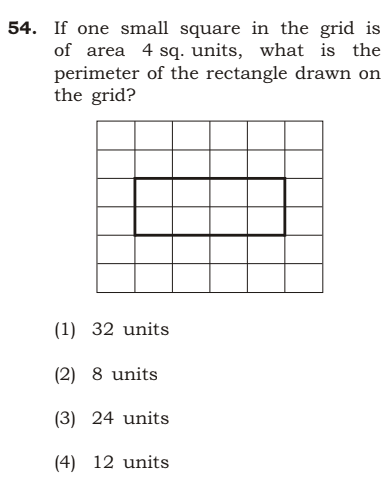
Ans: (3) 24 units.
- A child scored 75 marks in each of five subjects. What is the median marks obtained by the child?
(1) 75 (2) 375
(3) 15 (4) 70
Ans: (1) 75.
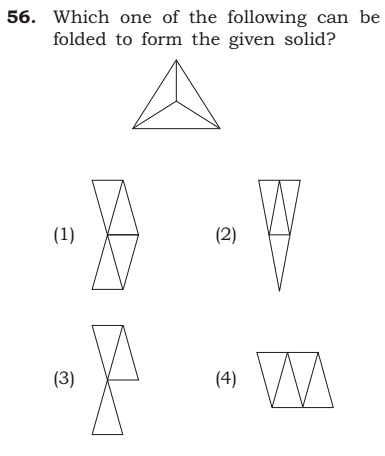
Ans: (2).
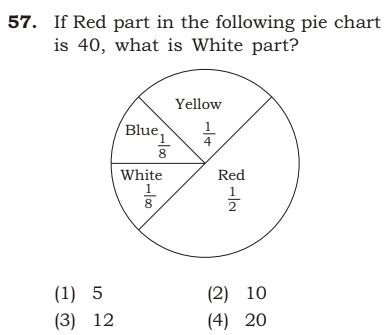
Ans: (2).
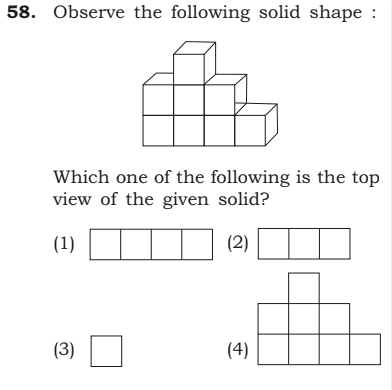
Ans: (1).
- Which one of the following costs more?
I. 200 packets of R250 each
II. 20 dozens of R250 each item
(1) I
(2) II
(3) Both I and II are equal
(4) Cannot be calculated
Ans: (2) II.
- The sum of 1-1+1-1+1-1L to even number of terms is—
(1) zero
(2) -1
(3) +1
(4) 2
Ans: (1) zero.
- What is the location of Jammu & Kashmir and Goa with respect to Bihar in India?
(1) East and West
(2) West and East
(3) North-west and South-west
(4) South-west and North-east
Ans: (3) North-west and South-west.
- Under which of the following conditions will the process of evaporation be slowest?
(1) Both surface area and temperature increase
(2) Surface area increases but temperature decreases
(3) Surface area decreases but temperature increases
(4) Both surface area and temperature decrease
Ans: (4) Both surface area and temperature decrease.
- The ability to understand relative position of places, distances and directions is—
(1) directional skill
(2) mapping skill
(3) positional skill
(4) graphic skill
Ans: (2) mapping skill.
- Which National Curriculum Framework (NCF) recommended Environmental Studies to be taught as an integrated curricular area at the primary level?
(1) NCF–2005
(2) NCF–1988
(3) NCF–2000
(4) NCF–1975
Ans: (4) NCF–1975.
- Which region has the practice of shifting cultivation in India?
(1) North-eastern region
(2) Southern region
(3) North-western region
(4) South-eastern region
Ans: (1) North-eastern region.
- Which one of the following statements is not true for hydropower generated from river dams?
(1) Dams encourage sustainable growth.
(2) It does not pollute water or air.
(3) Hydropower facilities can have large environmental impacts.
(4) Dams displace indigenous people from their river lifelines.
Ans: (1) Dams encourage sustainable growth.
- Which of the following is/are greenhouse gas/gases?
(1) Carbon dioxide
(2) Methane
(3) Water vapour
(4) All of the above
Ans: (4) All of the above.
- Why are cold deserts in India not affected by the monsoon?
(1) Cold deserts have hot summers and extremely cold winters.
(2) Cold deserts lie in the rain shadow of the Himalayas.
(3) Air is very thin in cold deserts.
(4) Cold deserts are at a very high altitude.
Ans: (2) Cold deserts lie in the rain shadow of the Himalayas.
- Which one of the following is responsible for turning Taj Mahal yellow?
(1) Nitrogen dioxide
(2) Sulphur dioxide
(3) Sulphur
(4) Chlorine
Ans: (2) Sulphur dioxide.
- Who built the Golconda Fort?
(1) Chola Dynasty
(2) Chalukya Dynasty
(3) Kakatiya Dynasty
(4) Pallava Dynasty
Ans: (3) Kakatiya Dynasty.
- What is the mass of an object with a density of 15 g/mL and a volume of 3 mL?
(1) 18 g
(2) 45 g
(3) 5 g
(4) 12 g
Ans: (2) 45 g.
- Which one of the following is a scalar quantity?
(1) Mass
(2) Gravity
(3) Momentum
(4) Weight
Ans: (1) Mass.
- An object in which no light rays can pass through is called—
(1) opaque
(2) translucent
(3) transparent
(4) convex
Ans: (1) opaque.
- What will be the weight of an object on the surface of the earth whose
mass is 10 kg on the moon’s surface?
(1) 60 kg
(2) 10 kg
(3) 60 N
(4) 10 N
Ans:
- The rate of dissolution of a solute depends on—
(1) pressure
(2) temperature
(3) surface area
(4) weight
Ans: (3) surface area.
- Sushma wants her students to be sensitized for ‘conservation of trees’. Which one of the following is the most suitable strategy to do so?
(1) Conducting a debate in classroom
(2) Group discussion
(3) Poster making
(4) Helping children to adopt and nurture a plant
Ans: (4) Helping children to adopt and nurture a plant.
- Abhay asked his students to do a survey in groups on diseases that people in their neighbourhood suffered from. The survey is not mentioned in the textbook. Which option is not relevant for this teaching-learning strategy?
(1) It provided opportunity to interact with community.
(2) It helped children connect learning with real life.
(3) It enabled children understand data handling and work together.
(4) It helped the community understand the diseases that they suffered from.
Ans: (4) It helped the community understand the diseases that they suffered from.
- To talk about emergency situations, Priya asked children’s experiences when they faced any emergencies. Children narrated their experiences
with fire, electric shock and road accidents. She asked questions, assessed their existing understandings and discussed safety aspects using resources such as road safety advertisements from newspapers and also used LPG and electric bill to discuss safety guidelines on fire and electric shock respectively. Which is the most appropriate approach that Priya employed?
(1) Cognitive approach
(2) Experiential learning approach
(3) Enquiry approach
(4) Humanistic approach
Ans: (3) Enquiry approach.
- ‘Community’ is an important teaching and learning resource, because—
(1) it is inexpensive and accessible
(2) elderly people are wise and have time
(3) it provides learning opportunity in real setting
(4) one can accept all knowledge available in the community uncritically
Ans: (3) it provides learning opportunity in real setting.
- In EVS teaching-learning, linking classroom learning to life outside school and enriching it implies—
(1) going beyond the textbooks
(2) linking textbooks to global environmental issues and concerns
(3) whole school approach
(4) going beyond curriculum
Ans: (1) going beyond the textbooks.
- To class III students, Rama taught that a father, mother and their children constitute nuclear family and if grandparents and other relatives stay along, then it is an extended family. What do you think
of this?
(1) The definition of a family is incorrect.
(2) Rama is insensitive towards her students.
(3) The teaching-learning approach is not inclusive.
(4) The concept of family has to be taught like this.
Ans: (3) The teaching-learning approach is not inclusive.
- Which of the following is/are activity/activities in EVS classroom?
(1) Picture reading
(2) Field visit
(3) Use of blackboard
(4) All of the above
Ans: (4) All of the above.
- Environmental Studies curriculum may lead to holistic learning of children if it is—
(1) integrated
(2) inclusive
(3) thematic
(4) All of the above
Ans: (4) All of the above.
- The EVS textbook has a chapter on snake charmer. It is intended to make children aware and be sensitized—
(1) that it is an illegal act
(2) for snake charmers as children do not see them often these days
(3) that snake charmers may not harm snakes and they need to be provided with alternatives before depriving them of their livelihoods
(4) that animal keeping is good source of livelihood
Ans: (3) that snake charmers may not harm snakes and they need to be provided with alternatives before depriving them of their livelihoods.
- Which is most relevant to the mid-day meal time in school?
(1) It has nothing to do with teaching-learning.
(2) It is a good teaching-learning opportunity for EVS teaching-learning.
(3) It is for children who come empty stomach to school.
(4) It wastes a lot of precious time of teaching-learning.
Ans: (2) It is a good teaching-learning opportunity for EVS teaching-learning.
- What does ‘learning without burden’ in the context of environmental studies imply?
(1) Less weight of schoolbag
(2) Less number of chapters in EVS textbooks
(3) Load of incomprehension needs to be reduced
(4) The EVS curriculum needs to be reduced to half
Ans: (3) Load of incomprehension needs to be reduced.
- What purpose does group learning serve in an EVS classroom?
(1) Boys and girls can learn separately
(2) To segregate high performers and low achieving students and to do remedial teaching
(3) To inculcate values of cooperation and working together to enable each child participate actively and learn
(4) To manage students easily and reduce workload
Ans: (3) To inculcate values of cooperation and working together to enable each child participate actively and learn.
- What is the full form of ‘BALA’ ?
(1) Brain Aided Learning Assignment
(2) Braille as Learning Aid
(3) Building as Learning Aid
(4) Braille Aided Learning Assessment
Ans: (3) Building as Learning Aid.
- What do ‘alternative frameworks’ mean?
(1) Textbook explanations of various physical phenomena
(2) Ideas that differ from the formally accepted explanations of the concepts
(3) Ideas presently held by scientists and social scientists
(4) All ideas that are firmly held by children
Ans: (2) Ideas that differ from the formally accepted explanations of the concepts.
- Women are weaker than men. It is a—
(1) myth
(2) scientific fact
(3) stereotype
(4) superstition
Ans: (1) myth.
Directions : Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow (Q. Nos. 91 to 99) by selecting the correct/most appropriate options.
When it comes to structures that are both majestic and well-fortified, the classic European castle is the pinnacle of design. Across the ages castles changed, developed, and eventually fell out of use, but they still command the fascination of our culture.
Castles were originally built in England by Norman invaders in 1066. As William the Conqueror advanced through England, he fortified key positions to secure the land he had taken. Castles also served as bases of operation for offensive attacks. Troops were summoned to, organized around, and deployed from castles. In this way castles served both offensive and defensive roles in military operations.
Not limited to military purposes, castles also served as offices from which the lord would administer control over his fiefdom. They would address disputes, handle business, feast, and enjoy festivities. In this way castles served as important social centres in medieval England. Castles also served as symbols of power.
The first castles constructed in England were made from earth and timber. Those who constructed them took advantage of natural features, such as hills and rivers, to increase defenses. Since these castles were constructed from wood, they were highly susceptible to attacks by fire. Wooden castles were gradually replaced by stone, which greatly increased the strength of these fortifications; however, being made from stone did not make these castles entirely fireproof. Attackers could hurl flaming objects into the castle through the windows or ignite the wooden doors.
The demise of castles can ultimately be attributed to gunpowder. During the
15th century, artillery became powerful enough to break through stone walls. This greatly undermined the military role of castles. Castles were then replaced by artillery forts that had no role in civil administration, and country houses that were indefensible. Though castles no longer serve their original purposes, remaining castles receive millions of visitors each year from those who wish to experience these majestic vestiges of a time long
passed.
- Which one of the following is not a function of castles as expressed
in the passage?
(1) Castles served both offensive and defensive purposes militarily.
(2) Castles served as symbols of power.
(3) Castles were important social centres in medieval England.
(4) Castles were the places where knights would keep their best horses.
Ans: (4) Castles were the places where knights would keep their best horses.
- Which one of the following best describes the main idea in Paragraph 2?
(1) It describes how and why William the Conqueror took control of England.
(2) It explains why castles were first built in England and the military purposes they served.
(3) It shows how Norman lords were often scared and frequently retreated.
(4) It details all of the purposes that English castles served.
Ans: (2) It explains why castles were first built in England and the military purposes they served.
- The original castles were first made from earth and timber because—
(1) it takes a lot more time and energy to build a stone castle
(2) it did not occur to people to build castles out of stone
(3) people did not realize how weak wooden castles would be against fire
(4) wooden castles were prettier than dirty stone castles
Ans: (1) it takes a lot more time and energy to build a stone castle.
- Wooden castles were converted to stone castles as—
(1) wooden castles take a long time to build
(2) wooden castles are uncomfortable
(3) stone castles offer better defense
(4) stone castles stay cooler in the summer
Ans: (3) stone castles offer better defense.
- Which one of the following best explains how gunpowder was the
nemesis of traditional castles?
(1) Wars were fought with guns and hiding in castles was no longer
necessary.
(2) Artillery forts with large cannons became more stylish than traditional castles.
(3) Defending castles grew difficult, since attackers could just shoot castle defenders.
(4) Cannons were able to knock down stone walls, so castles offered little protection.
Ans: (4) Cannons were able to knock down stone walls, so castles offered little protection.
- Which one of the following titles would best describe the content of this passage?
(1) William the Conqueror : Bringing Castles to England
(2) Defending the Castle : Technologies Used to Defend Medieval Castles
(3) A Short History of Castles : The Rise and Fall of Castles in England
(4) Fancy Living : Learning about Castles, Palaces and Fortresses
Ans: (3) A Short History of Castles : The Rise and Fall of Castles in England.
- Which one of the following is an opinion?
(1) Stone is more resistant to fire than wood.
(2) William the Conqueror built the first castles in England.
(3) It is unfortunate that castles no longer serve their original purposes.
(4) Castles were used as offices of administration during the Middle Ages.
Ans: (3) It is unfortunate that castles no longer serve their original purposes.
- Choose a word from the given options which means almost the same as the word ‘vestiges’ used in the passage.
(1) Reminder
(2) Outskirts
(3) Farrago
(4) Creation
Ans: (1) Reminder.
- Choose a word which serves as the antonym of the word ‘pinnacle’.
(1) Nadir
(2) Crest
(3) Apex
(4) Steeple
Ans: (1) Nadir.
Directions: Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow (Q. Nos. 100 to 105) by selecting the correct/most appropriate options.
My mother bore me in the southern wild, And I am black, but O ! my soul is white; White as an angel is the English child : But I am black as if bereav’d of light.
My mother taught me underneath a tree And sitting down before the heat of day, She took me on her lap and kissed me, And pointing to the east began to say.
Look on the rising sun : there God does live. And gives his light, and gives his heat away.
And flowers and trees and beasts and men receive. Comfort in morning joy in the noonday.
And we are put on earth a little space, That we may learn to bear the beams
of love, And these black bodies and this sun-burnt face Is but a cloud, and like a shady grove.
- ‘The Little Black Boy’ was born in—
(1) the desert wastes
(2) the servants’ house
(3) the southern wild
(4) the east coast
Ans: (3) the southern wild.
- ‘The Little Black Boy’ wished that he could be—
(1) educated
(2) older
(3) free
(4) white
Ans: (4) white.
- The mother of ‘the Little Black Boy’ says God put people on earth—
(1) to learn to endure his love
(2) to work off their sins
(3) to prepare them for future trials
(4) to learn how to treat one another as equals
Ans: (1) to learn to endure his love.
- The mother of ‘the Little Black Boy’ says his dark skin and face are—
(1) a blessing
(2) a veil
(3) a curse
(4) a cloud
Ans: (4) a cloud.
- The phrase ‘like a shady grove’ is—
(1) a metaphor
(2) a simile
(3) an example of alliteration
(4) a personification
Ans: (2) a simile.
- Through the phrase ‘as if bereav’d of light’, the poet hints at—
(1) low self-esteem of the child
(2) lack of hope for the future
(3) colour of the boy
(4) All of the above
Ans: (4) All of the above.
- Iconic mode of learning is based on the system of using—
(1) a variety of activities
(2) symbols
(3) images and diagrams
(4) different types of graph
Ans: (3) images and diagrams.
- While reading for comprehension, we understand that some pairs are
examples of homograph. Which one of the following is a homograph?
(1) warm/tepid [being neither too hot nor too cold]
(2) lead [metal]/lead [give direction]
(3) lead [give direction]/dead [mortal]
(4) mail [post]/male [gender]
Ans: (2) lead [metal]/lead [give direction].
- A ‘sight word’ is a vocabulary item—
(1) that needs proper visual understanding of the context
(2) that is to be learnt by heart
(3) that the reader recognizes and finds meaningful on sight without a complicated analysis
(4) that helps in judging the effectiveness of the author’s style
Ans: (3) that the reader recognizes and finds meaningful on sight without a complicated analysis.
- Which one of the following methods is suggested for teaching grammar at primary level?
(1) Deductive method
(2) Textbook method
(3) Inductive method
(4) Translation method
Ans: (3) Inductive method.
- Flower and Hayes regarded which one of the following skills as ‘problem-creating and solving skill’ ?
(1) Listening
(2) Speaking
(3) Reading
(4) Writing
Ans: (4) Writing.
- Find out the function word from the following.
(1) And
(2) Champion
(3) Handsome
(4) Seizing
Ans: (1) And.
- What do you mean by ‘review’ ?
(1) Guess
(2) Evaluation
(3) Critical evaluation
(4) Assessment
Ans: (3) Critical evaluation.
- Content words are called—
(1) functors
(2) grammatical words
(3) lexical words
(4) empty words
Ans: (3) lexical words.
- ‘Cloze’ means—
(1) finishing
(2) missing part
(3) close
(4) assessing
Ans: (2) missing part.
- The last stage of writing is—
(1) controlled writing
(2) guided writing
(3) free writing
(4) advanced writing
Ans: (4) advanced writing.
- The procedure of alphabetic method is—
(1) letters—words—phrases—sentences
(2) words—phrases—sentences—paragraph
(3) letters—words—sentences—paragraph
(4) letters—words—phrases—paragraph
Ans: (1) letters—words—phrases—sentences.
- “You ask, what has my government done for you? I can answer in two
words a lot !”
The question put up here is—
(1) rhetorical
(2) stylized
(3) a prompt
(4) explanatory
Ans: (1) rhetorical.
- According to the observation in the National Curriculum Framework
(NCF)–2005, English is a _language in India.
(1) second
(2) foreign
(3) first
(4) global
Ans: (1) second.
- Read the exchange :
Teacher : Shall we go out to the garden and find out the names of those flowers near the corridor?
Student : Yes, yes, yeah.
Teacher : Yes, Ma’am, please.
Here, the teacher—
(1) relates language function with politeness
(2) makes a polite suggestion to start reading
(3) confirms the student’s request
(4) offers an alternative language activity
Ans: (1) relates language function with politeness.
- Which one of the following helps in learning the second language
without using the printed text?
(1) Natural approach
(2) Language immersion
(3) Grammar-translation method
(4) Situational approach
Ans: (2) Language immersion.
Directions: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that
follow (Q. Nos. 121 to 129) by selecting the correct/most appropriate options.
Man who is believed to have evolved from apes, is a curious mixture of varied motives. He is not only the subject of needs but is also their creator. He not only seeks to satisfy his needs but also caters to his desire for beauty and grace. He is eager to satisfy his passion for more and more knowledge. Although in a general way, the maxim ‘necessity is the mother of invention’ is true, it is by no means the whole truth. Man is something much greater than an intelligent being using his intellect to make newer inventions from time to time. He has within him a spirit which is ever exhorting him to cut down his needs and learn to be happy with what he has. The real purpose underlying this maxim lies in its utility in the worldly sense. It tells us to be up and doing, not to be passive in our attitude to life. It asks us not to remain slaves of old habits and ways of life. We must face the new situations with a creative mind. Every new difficulty, every new problem,
which confronts us in life, can be tackled successfully with the spirit of
inventiveness.
- Which one of the following is not the whole truth according to the
passage?
(1) Man has a desire for beauty and grace.
(2) Necessity is the mother of invention.
(3) Man desires to cut down his needs and wants.
(4) Man learns to be happy with what he has.
Ans: (2) Necessity is the mother of invention.
- What does the maxim mentioned in the passage teach us?
(1) To be worldly in the strict sense of the term
(2) To be slave of our needs and wants
(3) To endeavour constantly to create new passions and desires
(4) To be active in life and do something to help mankind
Ans: (4) To be active in life and do something to help mankind.
- What does the spirit within man tell him to do?
(1) To be a mixture of varied motives
(2) To evaluate the situations intelligently
(3) To cut down his desires and passions
(4) To acquire more and more wealth and comforts
Ans: (3) To cut down his desires and passions.
- Which of the following statements is/are true in the context of the
passage?
I. Man should be passive in his attitude to life.
II. Spirit of inventiveness may not stand in good stead in solving
every new problem.
III. Man has a passion for more and more knowledge.
(1) Only I
(2) Only I and II
(3) Only III
(4) Only II and III
Ans: (3) Only III.
- Which one of the following is similar in meaning to the word ‘maxim’
as used in the passage?
(1) Principle
(2) Direction
(3) Value
(4) Observation
Ans: (1) Principle.
- Which one of the following is not the characteristic of man as per
the passage?
(1) Man has many needs and motives.
(2) Man creates many needs for himself.
(3) Man seeks to satisfy his needs.
(4) Man desires to have more and more comforts and money.
Ans: (4) Man desires to have more and more comforts and money.
- Which one of the following statements is not true as per the passage?
(1) Spirit of inventiveness will stand in good stead.
(2) Man is the subject of various wants.
(3) Man creates new needs because they are sometimes good or beautiful.
(4) Man’s inner spirit tells him to be on the look out for newer and
higher wants.
Ans: (4) Man’s inner spirit tells him to be on the look out for newer and
higher wants.
- Choose the word which is opposite in meaning to the word ‘seeks’ as
used in the passage.
(1) Deplores
(2) Avoids
(3) Vanishes
(4) Approaches
Ans: (2) Avoids.
- Which one of the following is similar in meaning to the word ‘exhorting’ as used in the passage?
(1) Urging
(2) Supporting
(3) Demanding
(4) Clarifying
Ans: (1) Urging.
Directions: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that
follow (Q. Nos. 130 to 135) by selecting the correct/most appropriate options.
Did you know that there is a fiber that is as flexible and lightweight as nylon yet five times stronger than steel? Did you know that this fabric is resistant to temperatures higher than 500 degrees Fahrenheit? Did you know that a woman invented this fiber? This miraculous fabric is called Kevlar and it is used to make everything from body armor to musical
instruments.
The year was 1964. There were gasoline shortages due to conflict in the Middle East. A Polish-American chemist named Stephanie Louise Kwolek was working for DuPont, an American chemical company. She and her group were trying to make a lightweight, yet durable fiber to be used
in tires. Lighter tires would allow vehicles to get better gas mileage, but the tires had to be strong enough to resist the wear and tear of the road. They had been working on the problem for some time and had little success, until Kwolek had a breakthrough.
Kwolek and her group were synthesizing or creating fibers to test. During one of the steps in the process, Kwolek created a milky white solution by mixing two chemicals that were often used in the process. This solution was usually thrown away, but Kwolek convinced one of the technicians to help her test it. They were amazed to discover that the fabric that Kwolek had created was not only more durable than nylon, it was more durable
than steel. Kwolek had invented Kevlar.
Kevlar is a remarkable fabric known for its strength and durability. Since its invention it has found its way into a wide variety of products. Kevlar is used in sporting equipment like bike tires, bowstrings and tennis racquets. It is used in musical instruments like drumheads, reeds and speaker cones. And it is used in protective gear like motorcycle safety jackets, gloves and shoes. However, Kevlar is best known for its ability to stop bullets.
Richard Armellino created the first Kevlar bulletproof vest in 1975. It contained 15 layers of Kevlar, which could stop handgun and shotgun bullets. The vest also had a steel plate over the heart, which made the vest strong enough to stop rifle rounds. Vests like Armellino’s were quickly picked up by police forces and it is estimated that by 1990, half of all
police officers in America wore bulletproof vests daily. By 2006, there were over 2000 documented police vest ‘saves’, or instances where officers were protected from deadly wounds by wearing bulletproof vests.
- Which one of the following is not a product that has been made
with Kevlar?
(1) Tennis racquets
(2) Bungee jumping cords
(3) Brake pads
(4) Body armor
Ans: (2) Bungee jumping cords.
- For which of the following characteristics is Kevlar known?
(1) Heat resistant
(2) Strength
(3) Durability
(4) All of the above
Ans: (4) All of the above.
- Which one of the following caused the search for a fabric like Kevlar?
(1) A shortage in the gasoline supply
(2) A desire to protect police officers
(3) The need to replace asbestos
(4) The want of better musical instruments
Ans: (1) A shortage in the gasoline supply.
- A vest made of 15 layers of Kevlar with no steel plates could stop all but which of the following rounds?
(1) Handgun rounds
(2) Shotgun pellets
(3) Rifle rounds
(4) It could stop all of the above
Ans: (3) Rifle rounds.
- How much stronger is Kevlar than steel?
(1) Half as strong
(2) As strong
(3) Five times as strong
(4) 200 times as strong
Ans: (3) Five times as strong.
- What product was Kwolek trying to improve when she invented Kevlar?
(1) Tires
(2) Milk
(3) Brake pads
(4) Armor
Ans: (1) Tires.
- The study of meaning in a language
is known as—
(1) syntax
(2) semantics
(3) morphology
(4) linguistics
Ans: (2) semantics.
- The teacher tells a story about animals. Children make animal
noises every time they hear the name of the animal. It is—
(1) total physical response
(2) communicative language teaching
(3) grammar translation
(4) reading approach
Ans: (1) total physical response.
- Any of a wide variety of exercises, activities or devices used in the
language classroom for realizing lesson objectives is known as—
(1) method
(2) technique
(3) syllabus
(4) approach
Ans: (2) technique.
- A test which is administered at the end of a language course for
remedial teaching is—
(1) diagnostic test
(2) placement test
(3) achievement test
(4) memory test
Ans: (1) diagnostic test.
- The practice of grammatical structures in a controlled manner can be done by—
(1) correcting wrong sentences produced by learners
(2) gap-filling grammar exercises
(3) writing paragraphs and essays
(4) explaining the use of particular structures
Ans: (2) gap-filling grammar exercises.
- “In the backyard, the dog barked and howled at the cat” is an example of—
(1) simple sentence
(2) sentence fragment
(3) complex sentence
(4) complex compound sentence
Ans: (1) simple sentence.
- Which one of the following methods of teaching cannot be used interchangeably with each other?
(1) Reference method
(2) Incidental method
(3) Direct method
(4) Correlative method
Ans: (3) Direct method.
- Which one of the following statements is true?
(1) All formative tasks are meant for assessment.
(2) Assignments need to be given as classwork followed by homework everyday to provide variety and practice.
(3) Formative assessment, to be effective, must be conducted only after teaching a lesson.
(4) While all formative tasks are meant for improving teaching learning, some are used for assessment too.
Ans: (4) While all formative tasks are meant for improving teaching learning, some are used for assessment too.
- Mother tongue influence can be effectively minimized in the
classroom by—
(1) using the mother tongue more often
(2) giving examples from the mother tongue
(3) giving a lot of exposure in the target language
(4) giving inputs from the target language in a simple, graded manner
Ans: (4) giving inputs from the target language in a simple, graded manner.
- Which one of the following sentences is a result of error arising out of
translation from our language to another?
(1) The teacher is giving examination.
(2) The students are giving their examination.
(3) My joy knew no bounds.
(4) Are you going by the train?
Ans: (2) The students are giving their examination.
- Reading skill can be developed best by—
(1) writing answers to questions on text
(2) focusing on the use of words from context in the text
(3) doing vocabulary exercises
(4) doing quizzes and playing word games
Ans: (2) focusing on the use of words from context in the text.
- Who would be the implementer of education?
(1) Teacher
(2) Education Department
(3) Student
(4) Curriculum
Ans: (1) Teacher.
- A listening stimulus—
(1) presents input to separate groups of students who gather again to share it
(2) is listening to a good commentary to review it
(3) enables students to discuss a set of criteria that they prioritize to complete and present a task
(4) presents an information gap activity such as giving directions
Ans: (4) presents an information gap activity such as giving directions.
- If a language teacher has taught a topic in the class and no student
asks questions in her class, then may be—
(1) students are not paying attention
(2) she had been an excellent teacher
(3) whatever was taught was beyond the comprehension of the students
(4) all the students are at a higher level of learning
Ans: (3) whatever was taught was beyond the comprehension of the students.
- The founder of Structural Grammar was—
(1) Newfield
(2) Chapman
(3) Chomsky
(4) Fries
Ans: (4) Fries.
CTET December 2018 Question Paper with Answers:
- CTET December 2018 Question Paper. (Paper 1 Main)
- CTET December 2018 Question Paper Answer Key. (Paper 1 Main)
- CTET December 2018 Question Paper. (Paper 2 Main)
- CTET December 2018 Question Paper Answer Key. (Paper 2 Main)








Comments (No)